...
WCS allows configuring the camera and the microphone from a browser. Let's see how this can be done and what parameters you can adjust when an audio and video stream is captured. We use the Media Devices web application as an example:
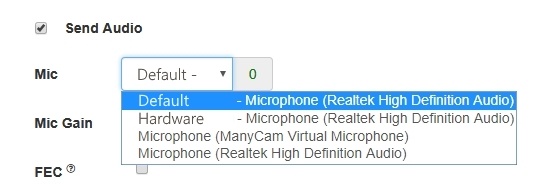
Microphone settings
1. Selecting the microphone from the list
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Flashphoner.getMediaDevices(null, true, MEDIA_DEVICE_KIND.INPUT).then(function (list) {
list.audio.forEach(function (device) {
...
});
...
}).catch(function (error) {
$("#notifyFlash").text("Failed to get media devices");
}); |
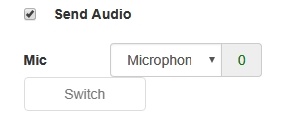
2. Microphone switching while stream is publishing
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$("#switchMicBtn").click(function (){
publishStreamstream.switchMic();.then(function(id) {
} $('#audioInput option:selected').prop('disabledselected', !($('#sendAudio').is(':checked'))); |
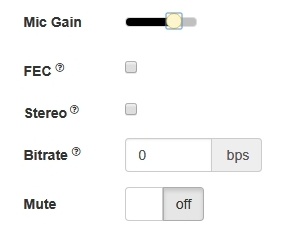
3. Adjusting microphone gain (works in Chrome only)
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$("#micGainControl").slider( false); $("#audioInput option[value='"+ id +"']").prop('selected', true); }).catch(function(e) { range: "min", console.log("Error " min: 0,+ e); max: 100,}); value: currentGainValue,}).prop('disabled', !($('#sendAudio').is(':checked'))); |
3. Adjusting microphone gain (works in Chrome only)
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$("#micGainControl").slider({ steprange: 10"min", animatemin: true0, slidemax: function (event, 100, value: currentGainValue, step: 10, animate: true, slide: function (event, ui) { currentGainValue = ui.value; if(previewStream) { publishStream.setMicrophoneGain(currentGainValue); } } }); |
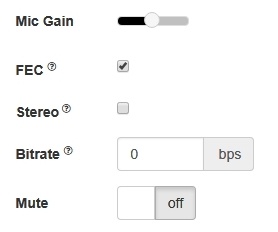
4. Enabling error correction (for the Opus codec only)
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (constraints.audio) {
constraints.audio = {
deviceId: $('#audioInput').val()
};
if ($("#fec").is(':checked'))
constraints.audio.fec = $("#fec").is(':checked');
...
} |
5. Setting stereo/mono mode.
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (constraints.audio) {
constraints.audio = {
deviceId: $('#audioInput').val()
};
...
if ($("#sendStereoAudio").is(':checked'))
constraints.audio.stereo = $("#sendStereoAudio").is(':checked');
...
} |
6. Setting audio bitrate in kbpsbps
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (constraints.audio) {
constraints.audio = {
deviceId: $('#audioInput').val()
};
...
if (parseInt($('#sendAudioBitrate').val()) > 0)
constraints.audio.bitrate = parseInt($('#sendAudioBitrate').val());
} |
7. Turning off the microphone (mute).
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if ($("#muteAudioToggle").is(":checked")) {
muteAudio();
}
|
Camera settings
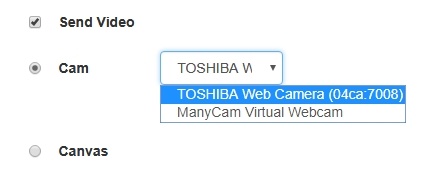
1. Camera selection
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Flashphoner.getMediaDevices(null, true, MEDIA_DEVICE_KIND.INPUT).then(function (list) {
...
list.video.forEach(function (device) {
...
});
}).catch(function (error) {
$("#notifyFlash").text("Failed to get media devices");
}); |
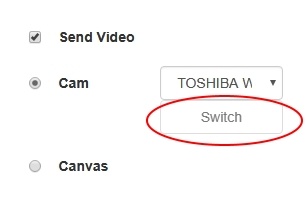
2. Switching cameras while stream is publishing
code:
...
If audio devices access should not be requested while choosing a camera, getMediaDevices() function should be called with explicit constraints setting
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$("#switchBtn").text("Switch").off('click').clickFlashphoner.getMediaDevices(null, true, MEDIA_DEVICE_KIND.INPUT, {video: true, audio: false}).then(function (list) { publishStream.switchCam();... }).prop('disabled', $('#sendCanvasStream').is(':checked')); |
Switching of the camera can be done "on the fly" during stream broadcasting. Here is how switching works:
- On PC cameras switch in the order they are defined in the device manager of the operating system.
- On Android, if Chrome is used, the default is the frontal camera. If Firefox is used, the default is the rear camera.
- On iOS in the Safari browser, by default the frontal camera is selected, but in the drop-down the rear camera is the first.
3. Specifying the resolution of the video
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
list.video.forEach(function (device) {
...
});
}).catch(function (error) {
$("#notifyFlash").text("Failed to get media devices");
}); |
2. Switching cameras while stream is publishing
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$("#switchBtn").text("Switch").off('click').click(function () { stream.switchCam().then(function(id) { constraints.video = {$('#videoInput option:selected').prop('selected', false); $("#videoInput option[value='"+ deviceId: $('#videoInput').val(),id +"']").prop('selected', true); width: parseInt($('#sendWidth').val()),}).catch(function(e) { console.log("Error " height: parseInt($('#sendHeight').val()) + e); }); if (Browser.isSafariWebRTC() && Browser.isiOS() && Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] === "WebRTC") { constraints.video.deviceId = {exact: $('#videoInput').val()}; constraints.video.width = {min: parseInt($('#sendWidth').val()), max: 640}; }); |
Switching of the camera can be done "on the fly" during stream broadcasting. Here is how switching works:
- On PC cameras switch in the order they are defined in the device manager of the operating system.
- On Android, if Chrome is used, the default is the frontal camera. If Firefox is used, the default is the rear camera.
- On iOS in the Safari browser, by default the frontal camera is selected, but in the drop-down the rear camera is the first.
3. Specifying the resolution of the video
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
constraints.video = { constraints.video.height = {mindeviceId: parseInt($('#sendHeight#videoInput').val()), max: 480}; } |
4. Setting FPS
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (constraints.video) { if (constraints.customStream) { width: parseInt($('#sendWidth').val()), ...height: parseInt($('#sendHeight').val()) } else {; if (Browser.isSafariWebRTC() && ... if (parseInt($('#fps').val()) > 0) Browser.isiOS() && Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] === "WebRTC") { constraints.video.frameRatedeviceId = {exact: parseInt($('#fps#videoInput').val())}; } } |
...
4. Setting video bitrate in kbpsFPS
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (constraints.video) {
if (constraints.customStream) {...
...
} else {
...
if (parseInt($('#sendVideoMinBitrate#fps').val()) > 0)
constraints.video.minBitrateframeRate = parseInt($('#sendVideoMinBitrate#fps').val());
} |
5.Setting video bitrate in kbps
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (constraints.video) { ... if (parseInt($('#sendVideoMaxBitrate#sendVideoMinBitrate').val()) > 0) constraints.video.maxBitrateminBitrate = parseInt($('#sendVideoMinBitrate').val()); if (parseInt($('#sendVideoMaxBitrate').val()); > 0) constraints.video.maxBitrate = parseInt($('#sendVideoMaxBitrate').val()); }... } |
6. Setting CPU Overuse Detection
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if (!$("#cpuOveruseDetection").is(':checked')) {
mediaConnectionConstraints = {
"mandatory": {
googCpuOveruseDetection: false
}
}
} |
7. Turning off the camera (mute)
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
if ($("#muteVideoToggle").is(":checked")) {
muteVideo();
} |
...
Local camera and microphone test is intended to check capturing in browser without publishing stream to server.
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
function startTest() {
if (Browser.isSafariWebRTC()) {
Flashphoner.playFirstVideo(localVideo, true);
Flashphoner.playFirstVideo(remoteVideo, false);
}
Flashphoner.getMediaAccess(getConstraints(), localVideo).then(function (disp) {
$("#testBtn").text("Release").off('click').click(function () {
$(this).prop('disabled', true);
stopTest();
}).prop('disabled', false);
window.AudioContext = window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext;
if (Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] == "WebRTC" && window.AudioContext) {
for (i = 0; i < localVideo.children.length; i++) {
if (localVideo.children[i] && localVideo.children[i].id.indexOf("-LOCAL_CACHED_VIDEO") != -1) {
var stream = localVideo.children[i].srcObject;
audioContextForTest = new AudioContext();
var microphone = audioContextForTest.createMediaStreamSource(stream);
var javascriptNode = audioContextForTest.createScriptProcessor(1024, 1, 1);
microphone.connect(javascriptNode);
javascriptNode.connect(audioContextForTest.destination);
javascriptNode.onaudioprocess = function (event) {
var inpt_L = event.inputBuffer..getChannelData(0);
}
var sum_L = 0.0;
}
}
for (var i = }0; elsei if (Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] == "Flash"< inpt_L.length; ++i) {
micLevelInterval = setInterval(function () {
sum_L += inpt_L[i] $("#micLevel").text(disp.children[0].getMicrophoneLevel())* inpt_L[i];
}, 500);
}
testStarted = true;
}).catch(function (error) {
$("#testBtn#micLevel").prop('disabled', falsetext(Math.floor(Math.sqrt(sum_L / inpt_L.length) * 100));
testStarted = false; }
});
}
drawSquare();
} |
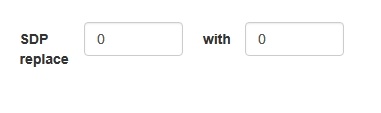
SDP parameters replacing
When publishing stream, there is a possibility to replace SDP parameters. In 'SDP replace' field string template is set for search for the parameter to replace, and in 'with' field new parameter value is set.
To replace SDP parameters, a callback function is used that should be set on stream creation in sdpHook option of createStream() method:
stream creation code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
previewStream = session.createStream( } } else if (Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] == "Flash") { micLevelInterval = setInterval(function () { name: streamName, $("#micLevel").text(disp.children[0].getMicrophoneLevel()); display: remoteVideo}, 500); } constraints: constraints, testStarted = true; }).catch(function (error) { sdpHook: rewriteSdp $("#testBtn").prop('disabled', false); ... testStarted = false; }) |
...
;
} |
SDP parameters replacing
When publishing stream, there is a possibility to replace SDP parameters. In 'SDP replace' field string template is set for search for the parameter to replace, and in 'with' field new parameter value is set.
To replace SDP parameters, a callback function is used that should be set on stream creation in sdpHook option of createStream() method:
stream creation code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
function rewriteSdp(sdp) { var sdpStringFind publishStream = $("#sdpStringFind").val();session.createStream({ var sdpStringReplace = $("#sdpStringReplace").val(); if (sdpStringFind != 0 && sdpStringReplace != 0) { name: streamName, display: localVideo, var newSDP = sdp.sdpString.toString();cacheLocalResources: true, newSDP = newSDP.replace(sdpStringFind, sdpStringReplace);constraints: constraints, mediaConnectionConstraints: mediaConnectionConstraints, return newSDP;sdpHook: rewriteSdp, } return sdp.sdpString; } |
Rising up the bitrate of video stream published in Chrome browser
SDP parameters replacement allows to rise video streeam published bitrate. To do this, SDP parameter 'a' must be replaced by this template:
...
}) |
rewriteSdp function code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
a=fmtp:(.*) (.*) |
to
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
a=fmtp:$1 $2;x-google-min-bitrate=2500 |
where 2500 is the bitrate in kilobytes per second.
Similarly, video bitrate on start can be set (x-google-start-bitrate attribute) and maximum bitrate can be limited (x-google-max-bitrate attribute). Note that if minimum bitrate only is set, then resulting bitrate cannot be above 2500 kbps, probably maximum bitrate value is fixed on this level by default in Chrome browser. When higher bitrate values are required, for example, to publish high reso;ution streams, both minimum and maximum values must be explicitly set:
| Code Block | |
|---|---|
| language | bashfunction rewriteSdp(sdp) {
var sdpStringFind = $("#sdpStringFind").val().replace('\\r\\n','\r\n');
var sdpStringReplace = $("#sdpStringReplace").val().replace('\\r\\n','\r\n');
if (sdpStringFind != 0 && sdpStringReplace != 0) {
var newSDP = sdp.sdpString.toString();
newSDP = newSDP.replace(new RegExp(sdpStringFind,"g"), sdpStringReplace);
return newSDP;
}
return sdp.sdpString;
} |
Rising up the bitrate of video stream published in Chrome browser
SDP parameters replacement allows to rise video streeam published bitrate. To do this, SDP parameter 'a' must be replaced by this template when publishing H264 stream:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
a=fmtp:(.*) (.*) |
to
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
a=fmtp:$1 $2;x-google-maxmin-bitrate=7000;2500 |
where 2500 is the bitrate in kilobytes per second.
Similarly, video bitrate on start can be set (x-google-
...
start-bitrate
...
In this case browser will try to keep bitrate in limits from 3000 to 7000 kbps when publishing a stream.
This feature is available in Chrome browser only.
Setting up codecs
When publishing the stream, there is a possibility to eliminate from WebRTC SDP codecs that should not be used to publish the given stream, for exampleattribute) and maximum bitrate can be limited (x-google-max-bitrate attribute). Note that if minimum bitrate only is set, then resulting bitrate cannot be above 2500 kbps, probably maximum bitrate value is fixed on this level by default in Chrome browser. When higher bitrate values are required, for example, to publish high reso;ution streams, both minimum and maximum values must be explicitly set:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
a=fmtp:$1 $2;x-google-max-bitrate=7000;x-google-min-bitrate=3000 |
In this case browser will try to keep bitrate in limits from 3000 to 7000 kbps when publishing a stream.
When publishing VP8 stream, SDP parameter 'a' must be replaced by this template
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
a=rtpmap:(.*) VP8/90000\r\n |
to
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
a=rtpmap:$1 VP8/90000\r\na=fmtp:$1 x-google-min-bitrate=3000;x-google-max-bitrate=7000\r\n |
This feature is available in Chrome browser only.
Bandwidth management
SDP parameters replacement allows to set bandwidth for stream publishhed. To do this, SDP parameter 'c' must be replaced by this template when publishing stream
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
c=IN (.*)\r\n |
to
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
c=IN $1\r\nb=AS:10000\r\n |
Setting up codecs
When publishing the stream, there is a possibility to eliminate from WebRTC SDP codecs that should not be used to publish the given stream, for example:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
publishStream = session.createStream({
...
stripCodecs: "h264,H264,flv,mpv"]
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (publishStream) {
...
});
publishStream.publish(); |
Such a capability is handy when you need to find some workaround for bugs of a browser or if it conflicts with the given codec. For example, if H.264 does not work in a browser, you can turn it off and switch to VP8 when working via WebRTC.
Sound device selection
Sound output device can be selected (and switched "on the fly") while stream is playing in Chrome and MS Edge browsers.
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Flashphoner.getMediaDevices(null, true, MEDIA_DEVICE_KIND.OUTPUT).then(function (list) {
list.audio.forEach(function (device) {
...
});
}).catch(function (error) {
$('#audioOutputForm').remove();
}); |
Note that Firefox and Safari browsers always return empty output devices list, therefore sound device setection does not supported for these browsers
WebRTC statistics displaying
A client application can get WebRTC statistics according to the standard while publishing or playing stream. The statistics can be displayed in browser, for example:
Note that in Safari browser audio only statistics can be displayed.
1. Statistics displaying while stream is published
stream.getStats() code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
publishStream.getStats(function (stats) {
if (stats && stats.outboundStream) {
if (stats.outboundStream.video) {
showStat(stats.outboundStream.video, "outVideoStat");
let vBitrate = (stats.outboundStream.video.bytesSent - videoBytesSent) * 8;
if ($('#outVideoStatBitrate').length == 0) {
let html = "<div>Bitrate: " + "<span id='outVideoStatBitrate' style='font-weight: normal'>" + vBitrate + "</span>" + "</div>";
$("#outVideoStat").append(html);
} else {
$('#outVideoStatBitrate').text(vBitrate);
}
videoBytesSent = stats.outboundStream.video.bytesSent;
...
}
if (stats.outboundStream.audio) {
showStat(stats.outboundStream.audio, "outAudioStat");
let aBitrate = (stats.outboundStream.audio.bytesSent - audioBytesSent) * 8;
if ($('#outAudioStatBitrate').length == 0) {
let html = "<div>Bitrate: " + "<span id='outAudioStatBitrate' style='font-weight: normal'>" + aBitrate + "</span>" + "</div>";
$("#outAudioStat").append(html);
} else {
$('#outAudioStatBitrate').text(aBitrate);
}
audioBytesSent = stats.outboundStream.audio.bytesSent;
}
}
...
}); |
2. Statistics displaying while stream is played
stream.getStats() code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
publishStream = session.createStream({ ... previewStream.getStats(function (stats) { stripCodecs: ["h264", "flv", "mpv"] if }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (publishStream(stats && stats.inboundStream) { ... }); publishStream.publish(); |
Such a capability is handy when you need to find some workaround for bugs of a browser or if it conflicts with the given codec. For example, if H.264 does not work in a browser, you can turn it off and switch to VP8 when working via WebRTC.
Sound device selection in Chrome browser
Sound output device can be selected (and switched "on the fly") while stream is playing in Chrome browser.
code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Flashphoner.getMediaDevices(null, true, MEDIA_DEVICE_KIND.OUTPUT).then(function (list) { if (stats.inboundStream.video) { showStat(stats.inboundStream.video, "inVideoStat"); let list.audio.forEach(function (device) { vBitrate = (stats.inboundStream.video.bytesReceived - videoBytesReceived) * 8; ... if ($('#inVideoStatBitrate').length == }0); { }).catch(function (error) { $('#audioOutputForm').remove(); }); |
WebRTC statistics displaying
A client application can get WebRTC statistics according to the standard while publishing or playing stream. The statistics can be displayed in browser, for example:
Note that in Safari browser audio only statistics can be displayed.
1. Statistics displaying while stream is published
stream.getStats() code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
publishStream.getStats(function (stats) {let html = "<div>Bitrate: " + "<span id='inVideoStatBitrate' style='font-weight: normal'>" + vBitrate + "</span>" + "</div>"; if (stats && stats.outboundStream) { if(stats.outboundStream.videoStats) {$("#inVideoStat").append(html); $('#outVideoStatBytesSent').text(stats.outboundStream.videoStats.bytesSent); } else { $('#outVideoStatPacketsSent').text(stats.outboundStream.videoStats.packetsSent); $('#outVideoStatFramesEncoded#inVideoStatBitrate').text(stats.outboundStream.videoStats.framesEncodedvBitrate); } else { videoBytesReceived = stats.inboundStream.video.bytesReceived; } ... if(stats.outboundStream.audioStats) { } $('#outAudioStatBytesSent').text(if (stats.outboundStreaminboundStream.audioStats.bytesSent); audio) { $('#outAudioStatPacketsSent').text(showStat(stats.outboundStream.audioStats.packetsSentinboundStream.audio, "inAudioStat"); } else { let aBitrate ... } = (stats.inboundStream.audio.bytesReceived - audioBytesReceived) * 8; } }); |
2. Statistics displaying while stream is played
stream.getStats() code:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
previewStream.getStats(function (statsif ($('#inAudioStatBitrate').length == 0) { if (stats && stats.inboundStream) { let html = "<div style='font-weight: bold'>Bitrate: " + if(stats.inboundStream.videoStats) { "<span id='inAudioStatBitrate' style='font-weight: normal'>" + aBitrate + "</span>" + "</div>"; $('#inVideoStatBytesReceived').text(stats.inboundStream.videoStats.bytesReceived); $('#inVideoStatPacketsReceived'"#inAudioStat").text(stats.inboundStream.videoStats.packetsReceivedappend(html); $('#inVideoStatFramesDecoded').text(stats.inboundStream.videoStats.framesDecoded); } else { ... } $('#inAudioStatBitrate').text(aBitrate); if(stats.inboundStream.audioStats) { } $('#inAudioStatBytesReceived').text(stats.inboundStream.audioStats.bytesReceived); audioBytesReceived $('#inAudioStatPacketsReceived').text(= stats.inboundStream.audioStatsaudio.packetsReceived)bytesReceived; } else {} ... } } }); |
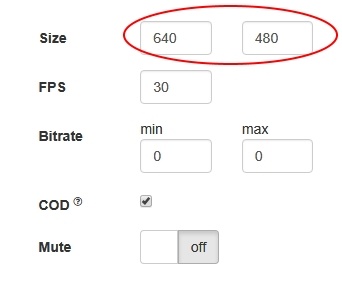
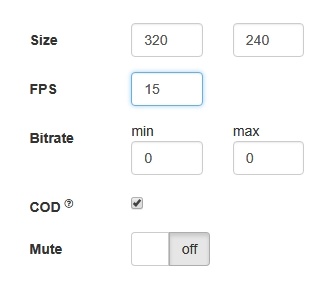
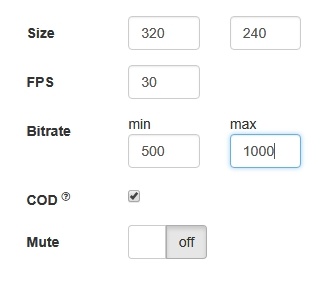
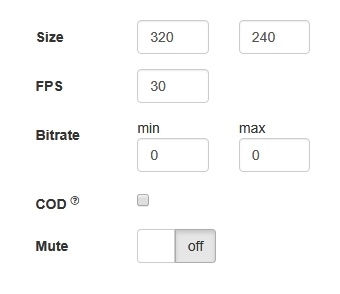
Picture parameters management
When video stream is published, it is possible to manage picture resolution and frame rate with constraints.
...
1. While streaming from chosen microphone and camera, when switch 'Screen share' is set to 'on' switchToScreen functioun will be invoked
stream.switchToScreen code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
function switchToScreen() {
if (publishStream) {
$('#switchBtn').prop('disabled', true);
$('#videoInput').prop('disabled', true);
publishStream.switchToScreen($('#mediaSource').val()).catch(function () {
$("#screenShareToggle").removeAttr("checked");
$('#switchBtn').prop('disabled', false);
$('#videoInput').prop('disabled', false);
});
}
} |
...
4. To revert back web camera streaming switchToCam function is invoked
stream.switchToCam code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
function switchToCam() {
if (publishStream) {
publishStream.switchToCam();
$('#switchBtn').prop('disabled', false);
$('#videoInput').prop('disabled', false);
}
} |
...