Overview
Supported platforms and browsers
Chrome 66+ | Firefox 59+ | Safari 14+ | MS Cromium Edge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Windows | + | + | + | |
Mac OS | + | + | + | |
Android | + | - | ||
iOS | + (iOS 14.6+) | - | + |
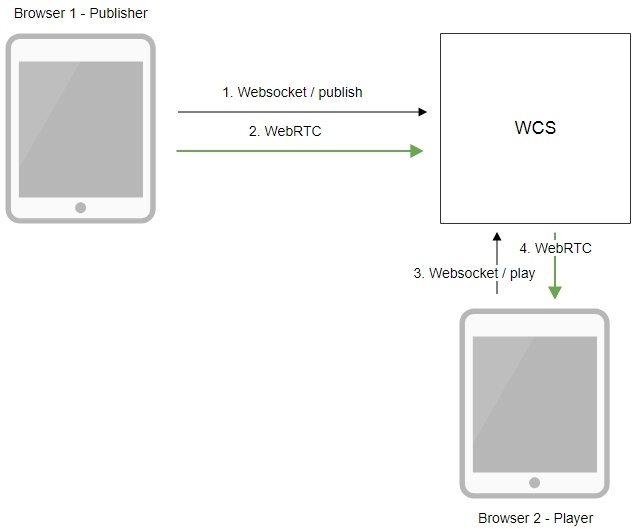
Operation flowchart
1. The browser establishes a connection to the server via the Websocket protocol and sends the publish command.
2. The browser captures the image of an HTML5 Canvas element and sends a WebRTC stream to the server.
3. The second browser establishes a connection also via Websokcet and sends the play command.
4. The second browser receives the WebRTC stream and plays the stream on the page.
Quick manual on testing
Capturing a video stream from HTML5 Canvas and preparing for publishing
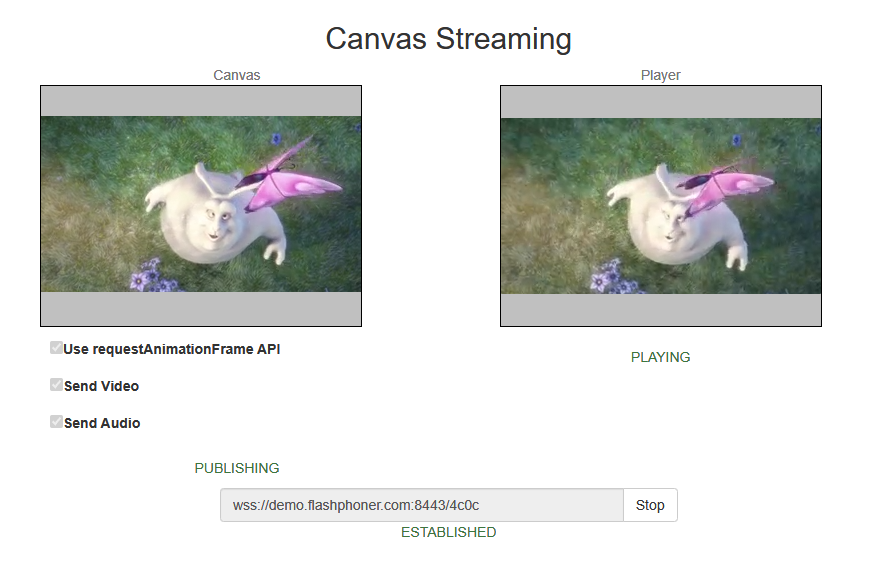
1. For test we use:
- WCS server demo.flashphoner.com
- Canvas Streaming web application in Chrome browser
2. Press "Start". This starts streaming from HTML5 Canvas on which test video fragment is played:
3. To make shure that stream goes to server, open chrome://webrtc-internals
4. Playback graphs chrome://webrtc-internals
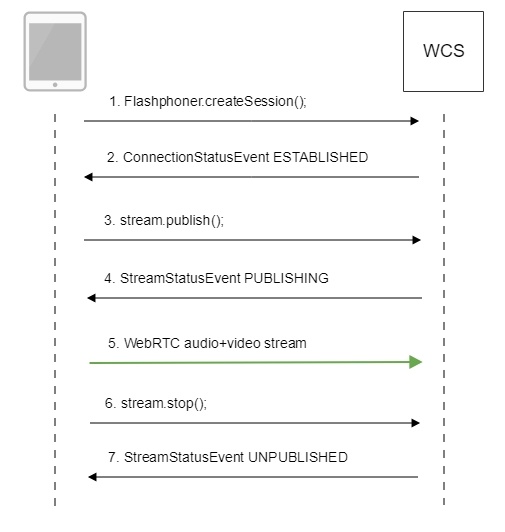
Call flow
Below is the call flow in the Canvas Streaming example
1. Establishing a connection to the server.
Flashphoner.createSession(); code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
//session connected, start streaming
startStreaming(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){
setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED);
onStopped();
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){
setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED);
onStopped();
});
2. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful connection.
ConnectionStatusEvent ESTABLISHED code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
//session connected, start streaming
startStreaming(session);
...
});
2.1. Set up and start HTML5 Canvas capturing
getConstraints(); code
function getConstraints() {
var constraints;
var stream = createCanvasStream();
constraints = {
audio: false,
video: false,
customStream: stream
};
return constraints;
}
createCanvasStream():
set up video capturing from Canvas code
function createCanvasStream() {
var canvasContext = canvas.getContext("2d");
var canvasStream = canvas.captureStream(30);
mockVideoElement = document.createElement("video");
mockVideoElement.setAttribute("playsinline", "");
mockVideoElement.setAttribute("webkit-playsinline", "");
mockVideoElement.src = '../../dependencies/media/test_movie.mp4';
mockVideoElement.loop = true;
mockVideoElement.muted = true;
...
return canvasStream;
}
draw on Canvas using requestAnimationFrame() or setTimeout() code
function createCanvasStream() {
...
var useRequestAnimationFrame = $("#usedAnimFrame").is(':checked');
mockVideoElement.addEventListener("play", function () {
var $this = this;
(function loop() {
if (!$this.paused && !$this.ended) {
canvasContext.drawImage($this, 0, 0);
if (useRequestAnimationFrame) {
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
} else {
setTimeout(loop, 1000 / 30); // drawing at 30fps
}
}
})();
}, 0);
...
return canvasStream;
}
play test video fragment on Canvas code
function createCanvasStream() {
...
mockVideoElement.play();
...
return canvasStream;
}
set up audio capturing from Canvas code
if ($("#sendAudio").is(':checked')) {
mockVideoElement.muted = false;
try {
var audioContext = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
} catch (e) {
console.warn("Failed to create audio context");
}
var source = audioContext.createMediaElementSource(mockVideoElement);
var destination = audioContext.createMediaStreamDestination();
source.connect(destination);
canvasStream.addTrack(destination.stream.getAudioTracks()[0]);
}
3. Publishing the stream.
stream.publish(); code
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
cacheLocalResources: true,
constraints: constraints
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function () {
...
}).publish();
4. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful publishing of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, status PUBLISHING code
session.createStream({
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING);
playStream();
onPublishing(stream);
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function () {
...
}).publish();
5. Sending the audio-video stream via WebRTC
6. Stopping publishing the stream.
stream.stop(); code
function stopStreaming() {
...
if (publishStream != null && publishStream.published()) {
publishStream.stop();
}
stopCanvasStream();
}
stopCanvasStream() code
function stopCanvasStream() {
if(mockVideoElement) {
mockVideoElement.pause();
mockVideoElement.removeEventListener('play', null);
mockVideoElement = null;
}
}
7. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful unpublishing of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, статус UNPUBLISHED code
session.createStream({
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED);
disconnect();
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function () {
...
}).publish();
To developer
Capability to capture video stream from an HTML5 Canvas element is available in WebSDK WCS starting from this version of JavaScript API. The source code of the example is located in examples/demo/streaming/canvas_streaming/.
You can use this capability to capture your own video stream rendered in the browser, for example:
var audioStream = new window.MediaStream();
var videoStream = videoElement.captureStream(30);
var audioTrack = videoStream.getAudioTracks()[0];
audioStream.addTrack(audioTrack);
publishStream = session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
constraints: {
customStream: audioStream
},
});
publishStream.publish();
Capturing from a video-element works in Chrome:
constraints.customStream = videoElement.captureStream(30);
Capturing from a canvas-element works in Chrome 66, Firefox 59 and Mac OS Safari 11.1:
constraints.customStream = canvas.captureStream(30);
Note that cacheLocalResources parameter is ignored and local resources are not cached while customStream is used.
Using requestAnimationFrame API
Since WebSDK build 2.0.200 the following example is added to use requestAnimationFrame API to draw image on HTML5 Canvas:
function createCanvasStream() {
...
var useRequestAnimationFrame = $("#usedAnimFrame").is(':checked');
mockVideoElement.addEventListener("play", function () {
var $this = this;
(function loop() {
if (!$this.paused && !$this.ended) {
canvasContext.drawImage($this, 0, 0);
if (useRequestAnimationFrame) {
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
} else {
setTimeout(loop, 1000 / 30); // drawing at 30fps
}
}
})();
}, 0);
...
return canvasStream;
}
This is modern method comparing to drawing by timer, but this requires a browser tab to be active while canvas stream is capturing. If user switches to another browser tab or minimizes browser window to background, requestAnimationFrame API will stop. Drawing by timer does not stop in this case excluding mobile browsers.
Known issues
1. Capturing from an HTML5 Video element does not work in Firefox on certain platforms and in old Safari versions.
Solution: use this capability only in the browsers supporting it.
2. In the Media Devices when performing HTML5 Canvas capturing:
- in Firefox, the local video does not display what is rendered;
- in Chrome, the local video does not display black background.
Solution: take browser specific behavior into account during development.
3. If the web applicaiton is inside an iframe element, publishing of the video stream may fail.
Symptoms: IceServer errors in the browser console.
Solution: put the app out of iframe to an individual page.
4. If publishing of the stream goes under Windows 10 or Windows 8 and hardware acceleration is enabled in the Google Chrome browser, bitrate problems are possible.
Symptoms: low quality of the video, muddy picture, bitrate shown in chrome://webrtc-internals is less than 100 kbps.
Solution: turn off hardware acceleration in the browser, switch the browser of the server to use the VP8 codec.
5. In some Chromium based browsers (Chrome, MS Edge) video is not publishing from canvas when hardware encoding acceleration is enabled
Symptoms; ther is no video in a stream published from a canvas, but there is audio only, streaming fails with Failed by Video RTP activity error
Solution: disable hardware acceleration in browser by setting the flag chrome://flags/#disable-accelerated-video-encode to Disable or use other browser
6. Canvas capturing may stop while switching to another browser tab or minimizing browser window
Symptoms: canvas stream is freezing while playing it, player does not receive video and audio packets
Solution: hold the browser tab in foreground while capturing canvas from it.
7. Stream publishing resolution cannot exceed the canvas size
Symptoms: stream publishing picture size is equal or less than HTML5 Canvas elemet on the page size (width x height)
Solution:
a) use HTML5 Canvas of appropriate size on the page to publish a desired resolution
b) transcode the stream picture to the desired size at server side