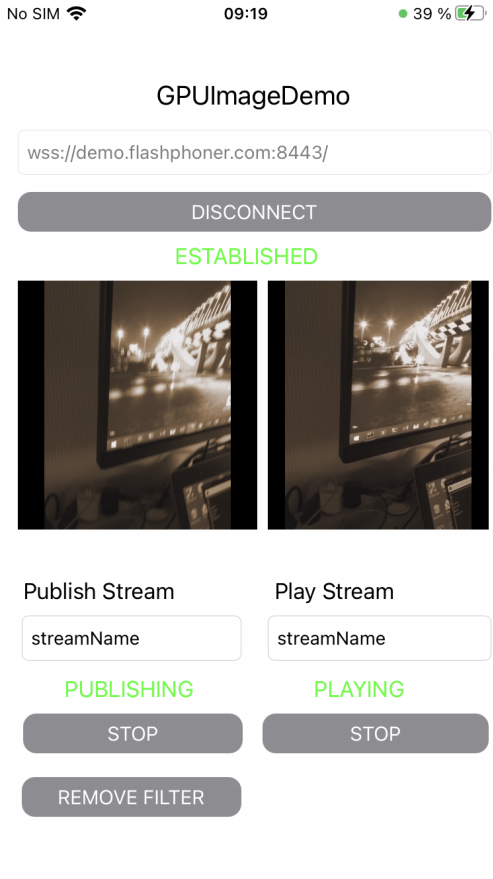
Example of video capturing using GPUImage library
The application shows how to capture video from custom source using GPUImage Swift luibrary implementation to apply filters.
On screenshot below, video is publishing with Monochrome filter applied frpm GPUImage kit
Inputs
- 'WCS URL', where demo.flashphoner.com is WCS server address
- 'Publish Stream' to input stream name to publish
- 'Play Stream' to input stream name to play
Beautify Apply Filter/Remove Filter button enables and disables the filter (the filter is enabled on screenshot)
Analyzing the code
To analyze the example code take ImageOverlaySwift example version which is available on GitHub:
- GPUImageDemoViewController - main application view class (implementation file GPUImageDemoViewController.swift)
- CameraVideoCapturer - class to implement video capturing and handling (implementation file CameraVideoCapturer.swift)
1. API import
import FPWCSApi2Swift
2. Video capturer initialization
var capturer: CameraVideoCapturer = CameraVideoCapturer()
3. Session creation and connecting to the server
WCSSession, WCSSession.connect code
The following session parameter are set:
- WCS server URL
- server backend application name defaultApp
@IBAction func connectPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(connectButton, false)
if (connectButton.title(for: .normal) == "CONNECT") {
if (session == nil) {
let options = FPWCSApi2SessionOptions()
options.urlServer = urlField.text
options.appKey = "defaultApp"
do {
try session = WCSSession(options)
} catch {
print(error)
}
}
...
changeViewState(urlField, false)
session?.connect()
} else {
session?.disconnect()
}
}
4. Stream publishing
WCSSession.createStream, WCSStream.publish code
The following parameters are passed to createStream method:
- stream name to publish
- local video view
- video capturer object
@IBAction func publishPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(publishButton,false)
if (publishButton.title(for: .normal) == "PUBLISH") {
let options = FPWCSApi2StreamOptions()
options.name = publishName.text
options.display = localDisplay.videoView
options.constraints = FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints(audio: true, videoCapturer: capturer);
do {
publishStream = try session!.createStream(options)
} catch {
print(error);
}
...
do {
try publishStream?.publish()
capturer.startCapture()
} catch {
print(error);
}
} else {
do {
try publishStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
5. Stream playback
WCSSession.createStream, WCSStream.play code
The following parameters are passed to createStream method:
- stream name to play
- remote video view
@IBAction func playPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(playButton,false)
if (playButton.title(for: .normal) == "PLAY") {
let options = FPWCSApi2StreamOptions()
options.name = playName.text;
options.display = remoteDisplay.videoView;
do {
playStream = try session!.createStream(options)
} catch {
print(error)
}
...
do {
try playStream?.play()
} catch {
print(error);
}
} else{
do {
try playStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
6. Stop stream playback
WCSStream.stop code
@IBAction func playPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(playButton,false)
if (playButton.title(for: .normal) == "PLAY") {
...
} else{
do {
try playStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
7. Stop stream publishing
WCSStream.stop code
@IBAction func publishPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(publishButton,false)
if (publishButton.title(for: .normal) == "PUBLISH") {
...
} else {
do {
try publishStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
8. Invoke filter application function
@IBAction func applyFilterPressed(_ sender: Any) {
if capturer.filter != nil {
capturer.applyFilter(nil)
applyFilterButton.setTitle("APPLY FILTER", for: .normal)
} else {
let filter = MonochromeFilter()
capturer.applyFilter(filter)
applyFilterButton.setTitle("REMOVE FILTER", for: .normal)
}
}
9. Applying filter
func applyFilter(_ filter: BasicOperation?) {
self.filter = filter
if let cam = self.camera, capturing {
cam.removeAllTargets()
self.gpuImageConsumer.removeSourceAtIndex(0)
if let fil = self.filter {
cam --> fil --> self.gpuImageConsumer
} else {
cam --> self.gpuImageConsumer
}
}
}
10. Receiving frame texture from camera
public func newTextureAvailable(_ texture:Texture, fromSourceIndex:UInt) {
// Ignore still images and other non-video updates (do I still need this?)
guard let frameTime = texture.timingStyle.timestamp?.asCMTime else { return }
// If two consecutive times with the same value are added to the movie, it aborts recording, so I bail on that case
guard (frameTime != previousFrameTime) else {
return
}
var pixelBufferFromPool:CVPixelBuffer? = nil
let pixelBufferStatus = CVPixelBufferCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault, texture.texture.width, texture.texture.height, kCVPixelFormatType_32BGRA, nil, &pixelBufferFromPool);
guard let pixelBuffer = pixelBufferFromPool, (pixelBufferStatus == kCVReturnSuccess) else {
return
}
CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, [])
renderIntoPixelBuffer(pixelBuffer, texture:texture)
capturer.captureOutput(pixelBuffer, time: frameTime)
CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, [])
}
11. Rendering frame texture to pixel buffer
func renderIntoPixelBuffer(_ pixelBuffer:CVPixelBuffer, texture:Texture) {
guard let pixelBufferBytes = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(pixelBuffer) else {
print("Could not get buffer bytes")
return
}
let mtlTexture = texture.texture;
guard let commandBuffer = sharedMetalRenderingDevice.commandQueue.makeCommandBuffer() else { fatalError("Could not create command buffer on image rendering.")}
commandBuffer.commit()
commandBuffer.waitUntilCompleted()
let bytesPerRow = CVPixelBufferGetBytesPerRow(pixelBuffer)
let region = MTLRegionMake2D(0, 0, mtlTexture.width, mtlTexture.height)
mtlTexture.getBytes(pixelBufferBytes, bytesPerRow: bytesPerRow, from: region, mipmapLevel: 0)
}