| Table of Contents |
|---|
Overview
Supported platforms and browsers
Chrome | Firefox | Safari 11 | Edge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Windows | + | + | + | |
Mac OS | + | + | + | |
Android | + | + | ||
iOS | - | - | + |
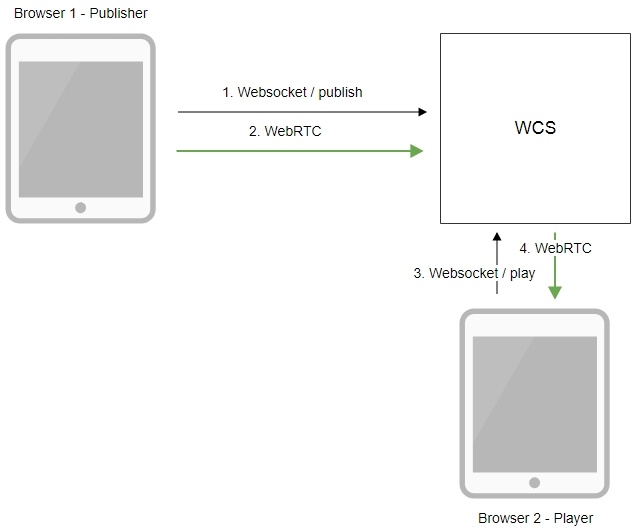
Operation flowchart
1. The browser connects to the server via the Websocket protocol and sends the publish command.
2. The browser captures the microphone and the camera and sends a WebRTC stream to the server.
3. The second browser establishes a connection also via Websocket and sends the play command.
4.The second browser receives the WebRTC stream and plays that stream on the page.
Quick manual on testing
Capturing a video stream from the web camera and preparing for publishing
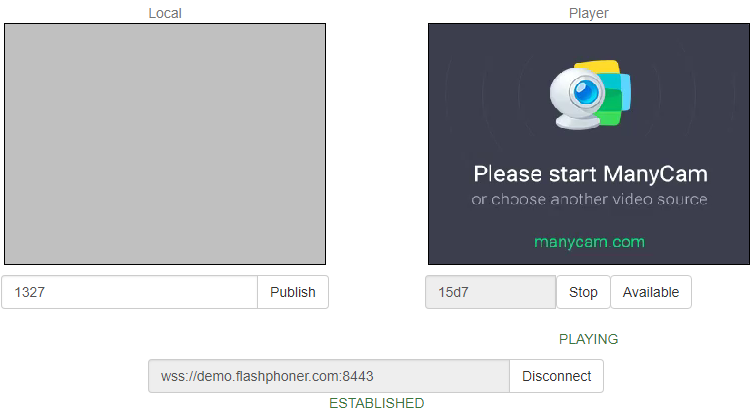
1. For this test we use the demo server at demo.flashphoner.com and the Two Way Streaming web application:
2. Establish a connection with the server by clicking the Connect button
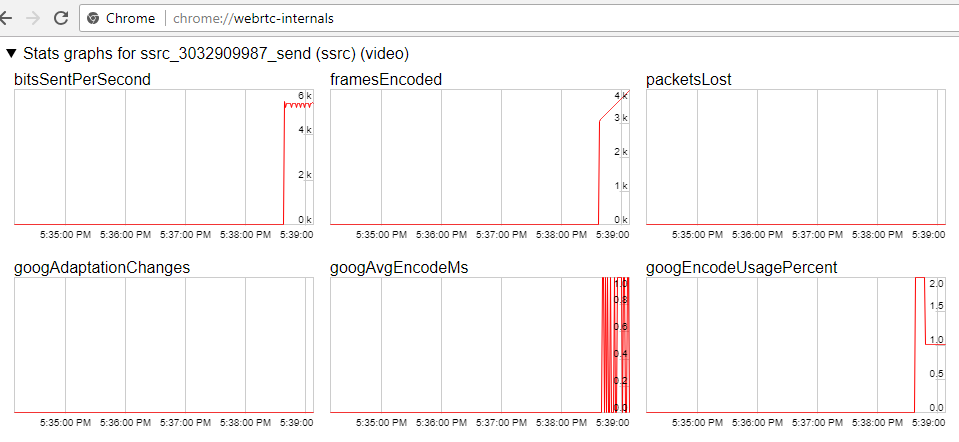
3. Click Publish. The browser captures the camera and sends the stream to the server.
4. Make sure the stream us sent to the server and the system operates normally by opening chrome://webrtc-internals
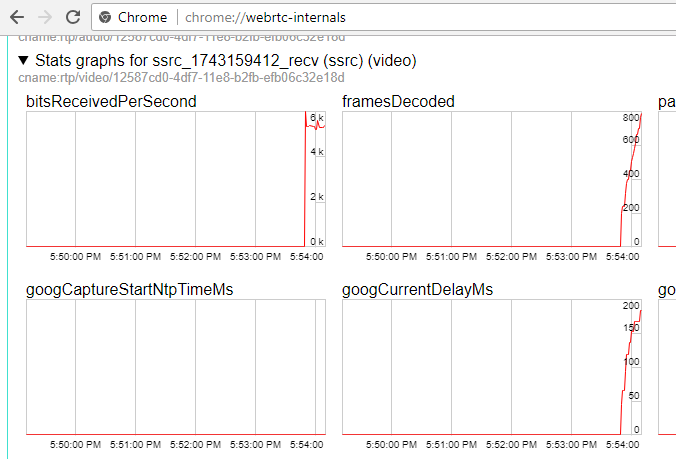
5. Open the Two Way Streaming app in a new window, click Connect and specify the stream ID, then click Play.
6. Playback diagrams in chrome://webrtc-internals
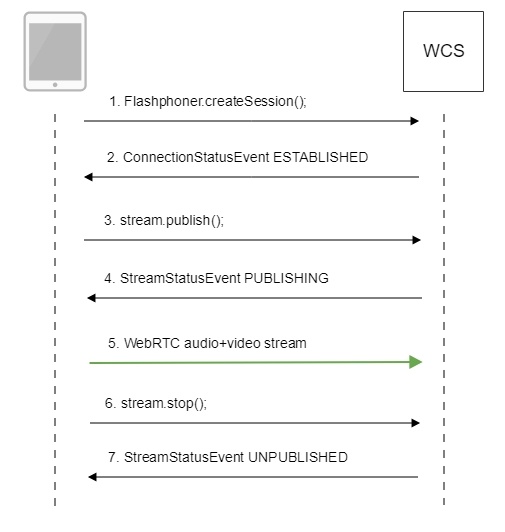
Call flow
Below is the call flow based on the Two Way Streaming example
1. Establishing connection to the server.
Flashphoner.createSession(); code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function (session) {
setStatus("#connectStatus", session.status());
onConnected(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function () {
setStatus("#connectStatus", SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED);
onDisconnected();
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function () {
setStatus("#connectStatus", SESSION_STATUS.FAILED);
onDisconnected();
}); |
2. Receiving from the server the successful connection status.
ConnectionStatusEvent ESTABLISHED code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function (session) {
setStatus("#connectStatus", session.status());
onConnected(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function () {
setStatus("#connectStatus", SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED);
onDisconnected();
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function () {
setStatus("#connectStatus", SESSION_STATUS.FAILED);
onDisconnected();
}); |
3. Publishing the stream.
stream.publish(); code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
cacheLocalResources: true,
receiveVideo: false,
receiveAudio: false
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING);
onPublishing(stream);
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED);
onUnpublished();
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function () {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.FAILED);
onUnpublished();
}).publish(); |
4. Receiving from the server the successful publishing status.
StreamStatusEvent, статус PUBLISHING code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
cacheLocalResources: true,
receiveVideo: false,
receiveAudio: false
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING);
onPublishing(stream);
...
}).publish(); |
5. Sending audio-video stream via WebRTC
6. Stopping publishing the stream.
stream.stop(); code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
function onPublishing(stream) {
$("#publishBtn").text("Stop").off('click').click(function () {
$(this).prop('disabled', true);
stream.stop();
}).prop('disabled', false);
$("#publishInfo").text("");
} |
7. Receiving from the server an even confirming successful unpublishing.
StreamStatusEvent, статус UNPUBLISHED code
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
cacheLocalResources: true,
receiveVideo: false,
receiveAudio: false
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () {
setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED);
onUnpublished();
...
}).publish(); |
Known issues
1. If the web app is inside an iframe element, publishing of the video stream may fail.
Symptoms: IceServer errors in the browser console.
Solution: put the app out of iframe to an individual page.
2. If publishing of the stream goes under Windows 10 or Windows 8 and hardware acceleration is enabled in the Google Chrome browser, bitrate problems are possible.
Symptoms: low quality of the video, muddy picture, bitrate shown in chrome://webrtc-internals is less than 100 kbps.
Solution: turn off hardware acceleration in the browser, switch the browser of the server to use the VP8 codec.
1. The browser connects to the server via the Websocket protocol and sends the publish command.
2. The browser captures the microphone and the camera and sends a WebRTC stream to the server.
3. The second browser establishes a connection also via Websocket and sends the play command.
4.The second browser receives the WebRTC stream and plays that stream on the page.