The combination of WebSocket + HTML5 Canvas technologies is recommended to use for playing a video stream if a client browser does not support WebRTC and latency must be minimal. You can find thorough description of the WSPlayer player based on these technologies in this article.
Overview
Not all browsers have support for WebRTC. For example, the main method to deliver a live video stream to the Safari browser under iOS 9 and iOS 10 is HLS (HTTP Live Streaming). This protocol can lead to latencies more than 15 seconds.
Web Call Server sends a video stream to a browser via the Websocket protocol, which allows reducing latency down to 1-3 seconds and produces real time video in comparison with HLS. The stream is played in a browser using the Canvas HTML5 element.
Supported platforms and browsers
Chrome | Firefox | Safari 11 | Edge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Windows | + | + | + | |
Mac OS | + | + | + | |
Android | + | + | ||
iOS | - | - | + |
Supported codecs
- Video: MPEG
- Audio: G.711
Operation flowchart
- The browser connects to the server via the Websocket protocol and sends the publish command.
- The browser captures the microphone and the camera and sends the WebRTC stream to the server.
- The second browser establishes connection also via Websocket and sends the play command.
- The second browser receives the MPEG + G.711 stream via Websocket and plays this stream on the page using HTML5 Canvas.
Quick manual on testing
Publishing a video stream on the server and playing it using HTML5 + Canvas (WSPlayer) in a browser
1. For this test we use:
- the demo server at demo.flashphoner.com;
- the Two Way Streaming web application to publish the stream
- the Player web applicatiion to play the stream
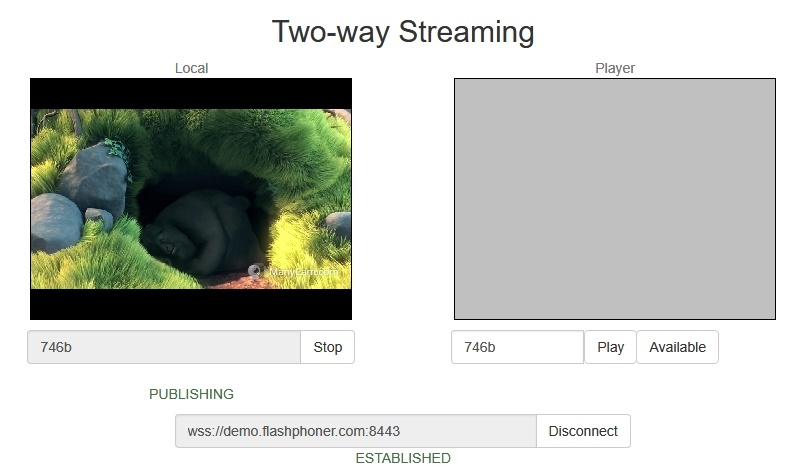
2. Open the Two Way Streaming web app. Click Connect, then click Publish. Copy the identifier of the stream:
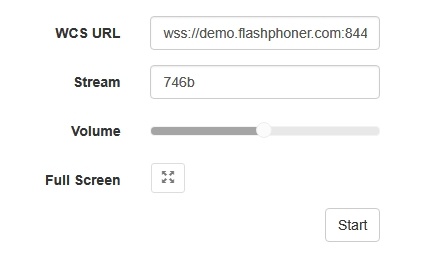
3. Open the Player web application and specify WSPlayer in the parameters of the URL
4. In the Stream field enter the identifier of the stream:
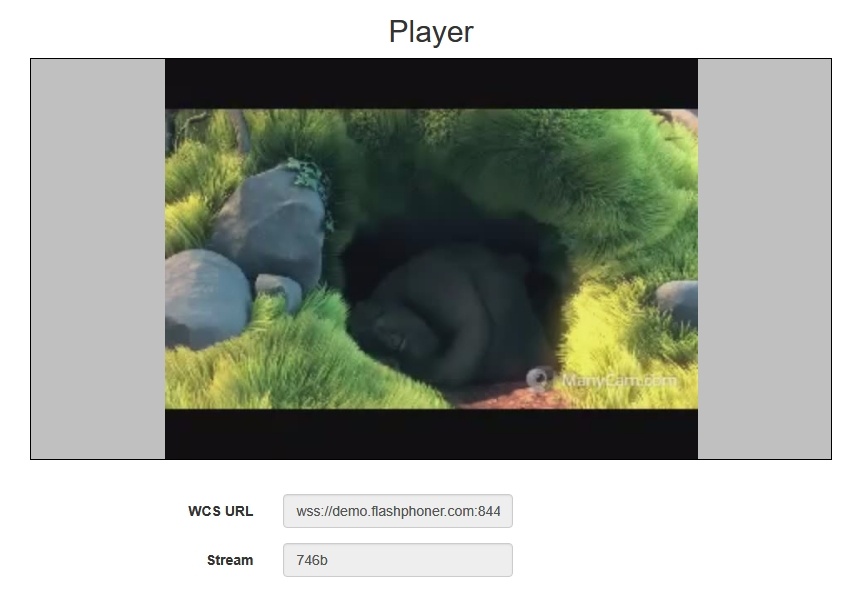
5. Click the Start button. The stream starts playing:
Call flow
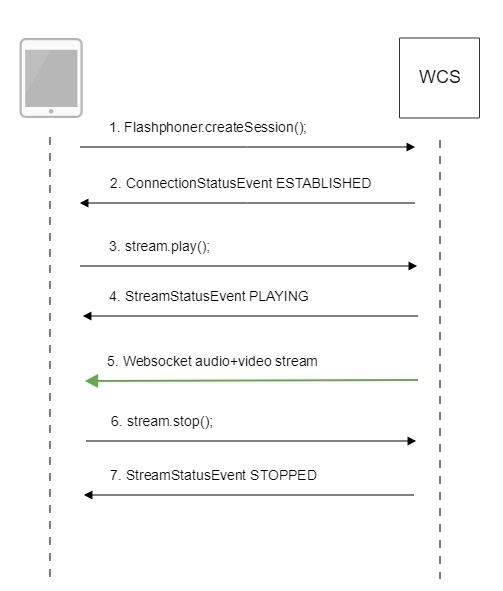
Below is the call flow when using the Player example to play the stream using WSPlayer.
1. Establishing connection to the server.
init(): code
if (Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] == "WSPlayer") {
resolution_for_wsplayer = {playWidth:640,playHeight:480};
}
Flashphoner.createSession(); code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
setStatus(session.status());
//session connected, start playback
playStream(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){
setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED);
onStopped();
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){
setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED);
onStopped();
});
2. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful connection.
ConnectionStatusEvent ESTABLISHED code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
setStatus(session.status());
//session connected, start playback
playStream(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){
...
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){
...
});
3. Playing the stream.
stream.play(); code
if (Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] === "MSE" && mseCutByIFrameOnly) {
...
}
if (resolution_for_wsplayer) {
options.playWidth = resolution_for_wsplayer.playWidth;
options.playHeight = resolution_for_wsplayer.playHeight;
} else if (resolution) {
...
}
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) {
...
});
stream.play();
4. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful playing of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, status PLAYING code
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) {
$("#preloader").show();
setStatus(stream.status());
onStarted(stream);
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.NOT_ENOUGH_BANDWIDTH, function(stream){
...
});
stream.play();
5. Receiving the audio and video stream via Websocket and playing via MSE
6. Stopping the playback of the stream.
stream.stop(); code
function onStarted(stream) {
$("#playBtn").text("Stop").off('click').click(function(){
$(this).prop('disabled', true);
stream.stop();
}).prop('disabled', false);
...
}
7. Receiving from the server an event confirming the playback of the stream is stopped.
StreamStatusEvent, status STOPPED code
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() {
setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED);
onStopped();
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.NOT_ENOUGH_BANDWIDTH, function(stream){
...
});
stream.play();
Known issues
1. Fullscreen mode is not supported for WSPlayer in iOS
Symptoms: Stream.fullScreen() call does not switch playback to full screen mode using WSPlayer mediaprovider
Solution: if possible, update device to latest iOS version and use WebRTC in Safari browser