WCS offers possibility to capture a media stream from an MP4 file located on the local disk of the server (Video on Demand, VOD). The received stream can be played, republished, managed just like any stream on the WCS server. First of all, this option is intended to play previously recorded broadcasts in a browsers or a mobile application on the client side.
Overview
To capture VOD from a file, specify a link to the vod file as a stream name when calling the session.createStream() function, as follows:
vod://sample.mp4
where sample.mp4 - is the name of the file that should be located in the /usr/local/FlashphonerWebCallServer/media/ directory.
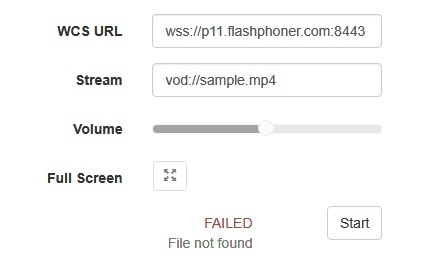
If a file with such a name does not exist, the server returns the StreamStatusEvent FAILED message, where the "info" field has the reason: "File not found".
A stream created this way can be displayed to one user (personal VOD). If a full-featured online-broadcast is required, provide the link to a file as follows:
vod-live://sample.mp4
Multiple user can connect to such a stream simultaneously.
Supported formats and codecs
- Container: MP4
- Video: H.264
- Audio: AAC
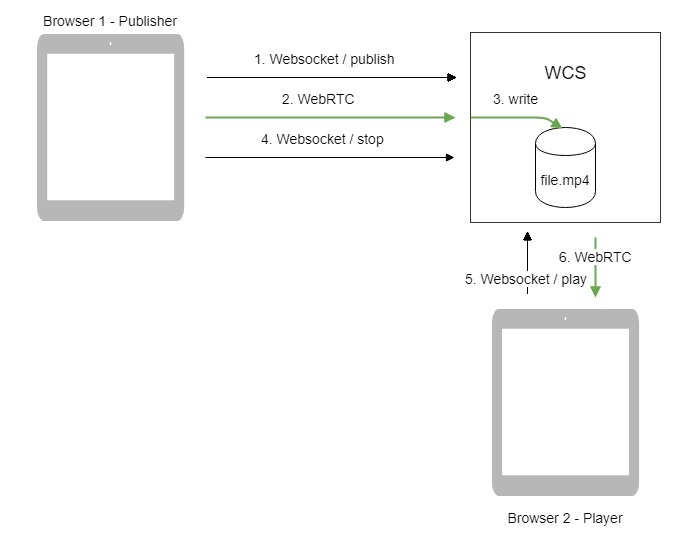
Operation flowchart
- The browser connects to the server via Websocket and sends the publish command.
- The browser captures the microphone and the camera and sends the WebRTC stream as H.264 + AAC to the server, enabling recording with the parameter record: true.
- The WCS server records the stream to a file.
- The browser stops publishing.
- The second browser establishes a connection via Websocket, creates a stream, specifies the file name, and sends the play command.
- The second browser receives the WebRTC stream and plays this stream on the page.
Quick manual on testing
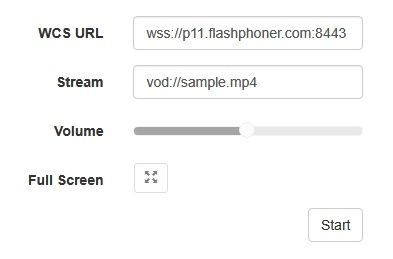
1. For the test we use the Player web application to play the file.
2. Upload the file to the /usr/local/FlashphonerWebCallServer/media/ directory.
3. Open the Player web application and enter the name of the file in the Stream field:
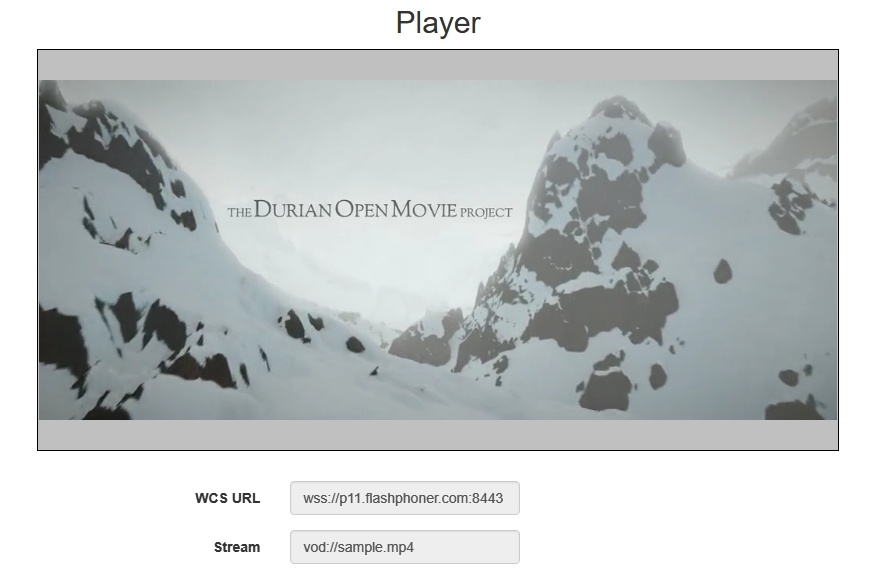
4. Click Start. The file starts playing:
5. Click Stop to stop the playback.
6. Delete the file from /usr/local/FlashphonerWebCallServer/media/
7. Click Start. You should see the FAILED status and the "File not found" message:
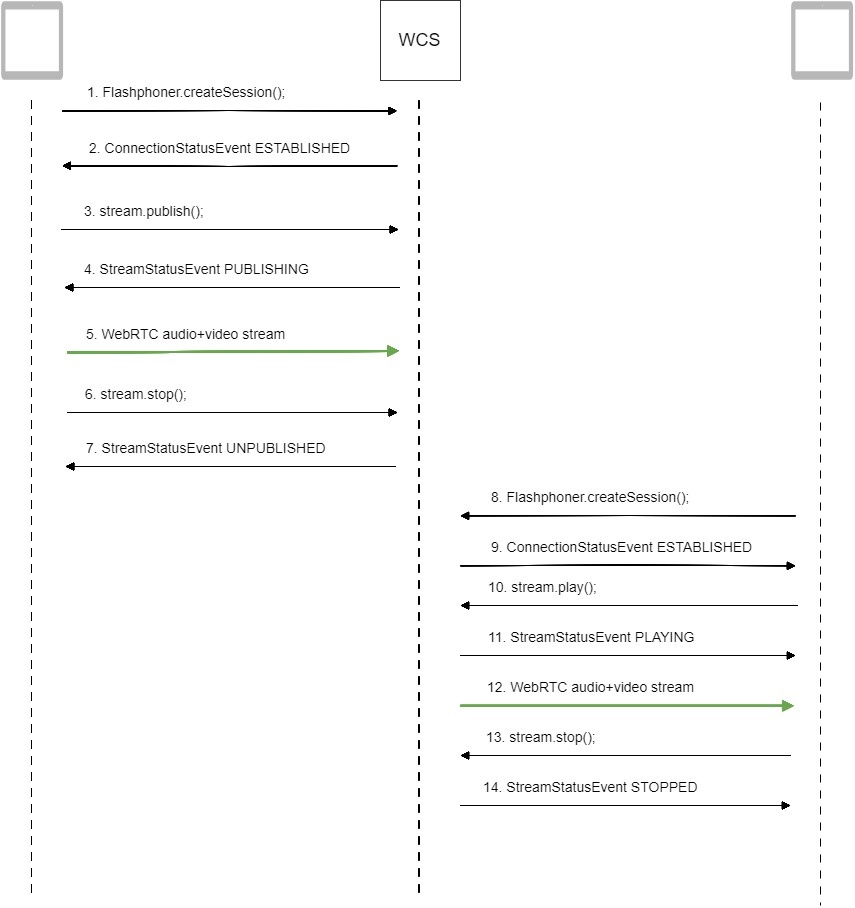
Call flow
Below is the call flow when using:
the Stream Recording example to publish the stream and record the file
the Player example to play the VOD stream
1. Establishing a connection to the server to publish and record the stream.
Flashphoner.createSession(); code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
...
});
2. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful connection.
ConnectionStatusEvent ESTABLISHED code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
setStatus(session.status());
//session connected, start playback
publishStream(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){
...
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){
...
});
3. Publishing the stream with recording enabled.
stream.publish(); code
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
record: true,
receiveVideo: false,
receiveAudio: false
...
}).publish();
4. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful publishing of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, status PUBLISHING code
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
record: true,
receiveVideo: false,
receiveAudio: false
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function(stream) {
setStatus(stream.status());
onStarted(stream);
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) {
...
}).publish();
5. Sending audio and video stream via WebRTC.
6. Stopping publishing the stream.
stream.stop(); code
function onStarted(stream) {
$("#publishBtn").text("Stop").off('click').click(function(){
$(this).prop('disabled', true);
stream.stop();
}).prop('disabled', false);
}
7. Receiving from the server an event confirming unpublishing of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, status UNPUBLISHED code
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: localVideo,
record: true,
receiveVideo: false,
receiveAudio: false
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function(stream) {
setStatus(stream.status());
showDownloadLink(stream.getRecordInfo());
onStopped();
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) {
...
}).publish();
8. Establishing a connection to the server to play the stream.
Flashphoner.createSession(); code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
...
});
9. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful connection.
ConnectionStatusEvent ESTABLISHED code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
setStatus(session.status());
//session connected, start playback
playStream(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){
...
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){
...
});
10. Playing the stream.
stream.play(); code
if (Flashphoner.getMediaProviders()[0] === "MSE" && mseCutByIFrameOnly) {
options.mediaConnectionConstraints = {
cutByIFrameOnly: mseCutByIFrameOnly
}
}
if (resolution_for_wsplayer) {
options.playWidth = resolution_for_wsplayer.playWidth;
options.playHeight = resolution_for_wsplayer.playHeight;
} else if (resolution) {
options.playWidth = resolution.split("x")[0];
options.playHeight = resolution.split("x")[1];
}
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) {
...
});
stream.play();
11. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful playing of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, status PLAYING code
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) {
$("#preloader").show();
setStatus(stream.status());
onStarted(stream);
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.NOT_ENOUGH_BANDWIDTH, function(stream){
...
});
stream.play();
12. Receiving of the audio-video stream via Websocket and playing it via WebRTC
13. Stopping publishing the stream.
stream.stop(); code
function onStarted(stream) {
$("#playBtn").text("Stop").off('click').click(function(){
$(this).prop('disabled', true);
stream.stop();
}).prop('disabled', false);
...
}
14. Receiving from the server an event confirming successful stopping of the playback of the stream.
StreamStatusEvent, status STOPPED code
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() {
setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED);
onStopped();
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) {
...
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.NOT_ENOUGH_BANDWIDTH, function(stream){
...
});
stream.play();