Example of iOS application managing media devices
This example allows to publish WebRTC stream on Web Call Server and demonstrates selection of source camera and specification of the following parameters for published and played video
- resolution (width, height)
- bitrate
- FPS (Frames Per Second) - for published video
- quality - for played video
As well as publishing streams with audio and video, it allows to publish audio-only and video-only streams.
Audio and video can be muted when publishing is started (if corresponding controls has been set to ON before streaming was started), or while stream is being published.
Video streams can be played with or without video.
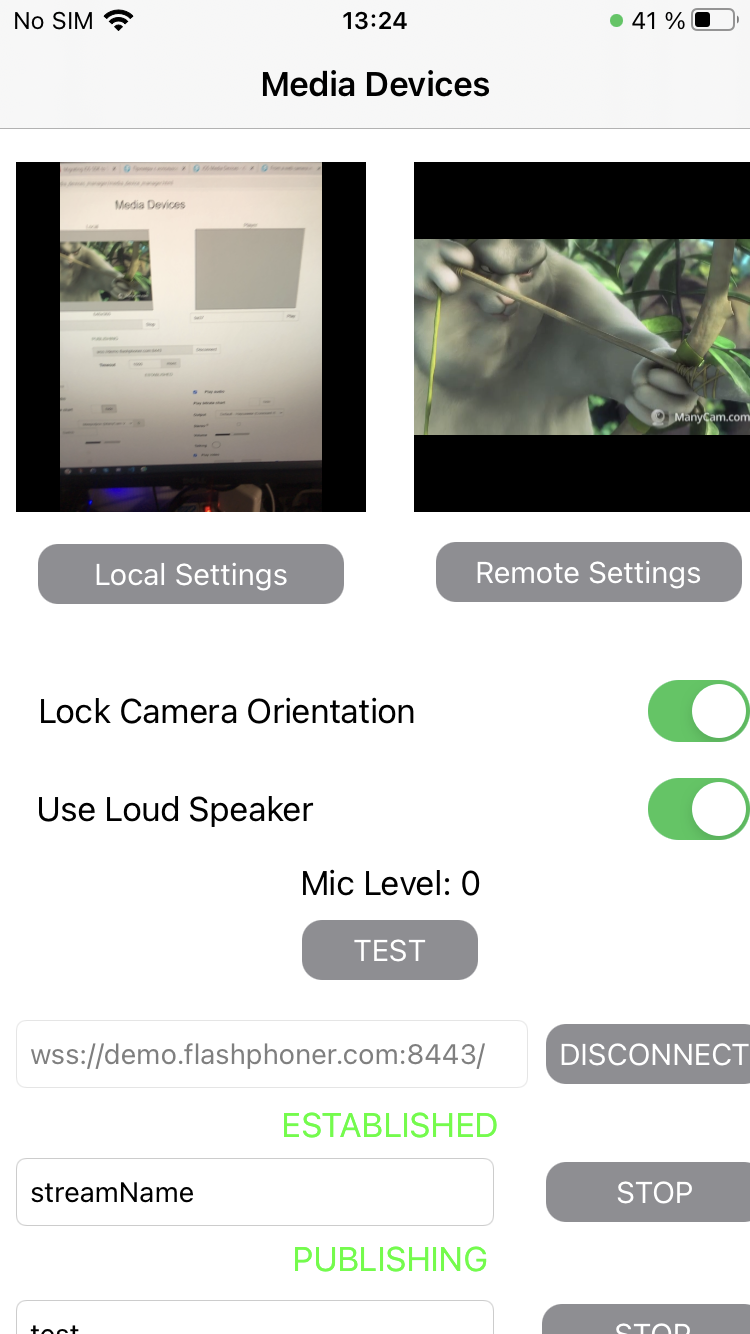
On the screenshot below the example is displayed when a stream is being published and played.
In the URL specified in the input field, demo.flashphoner.com is the address of the WCS server.
Two videos are displayed
- left - video from the camera
- right - the published video stream is played from the server
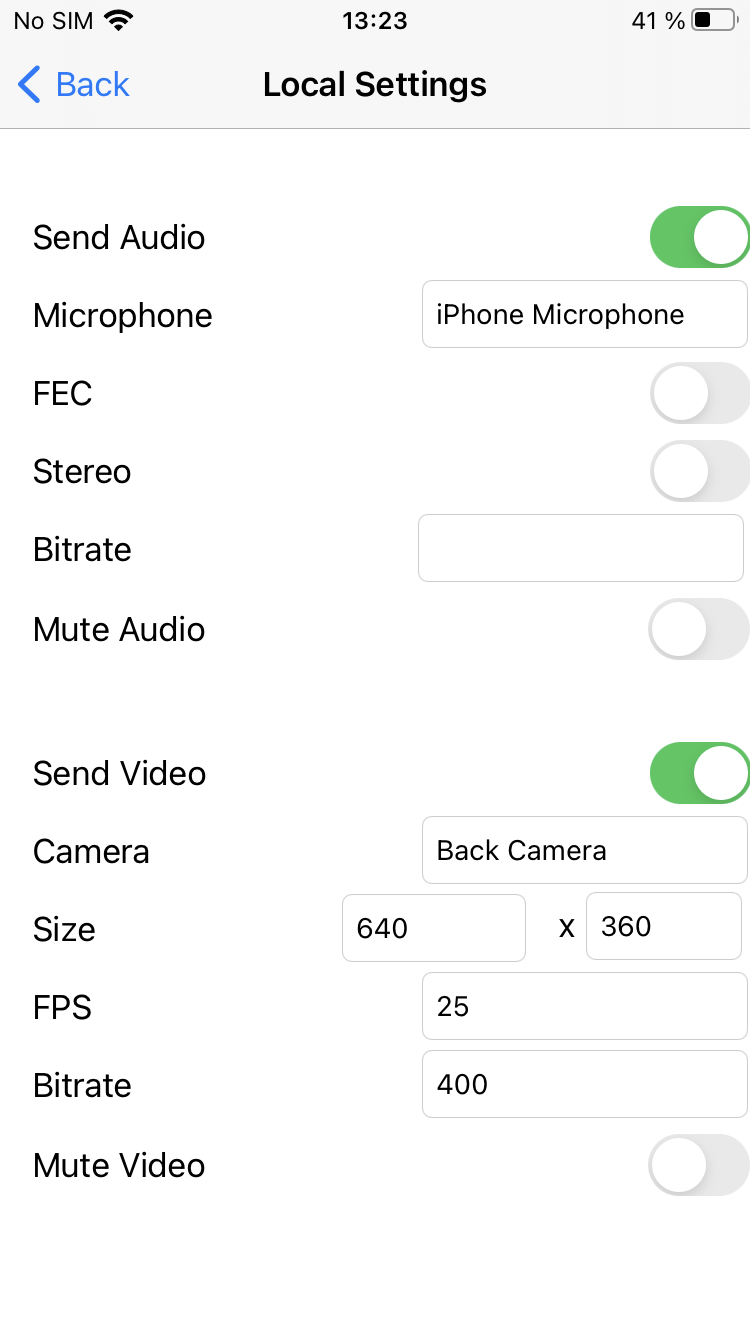
View with controls for publishing settings is displayed when 'Local settings' button is tapped
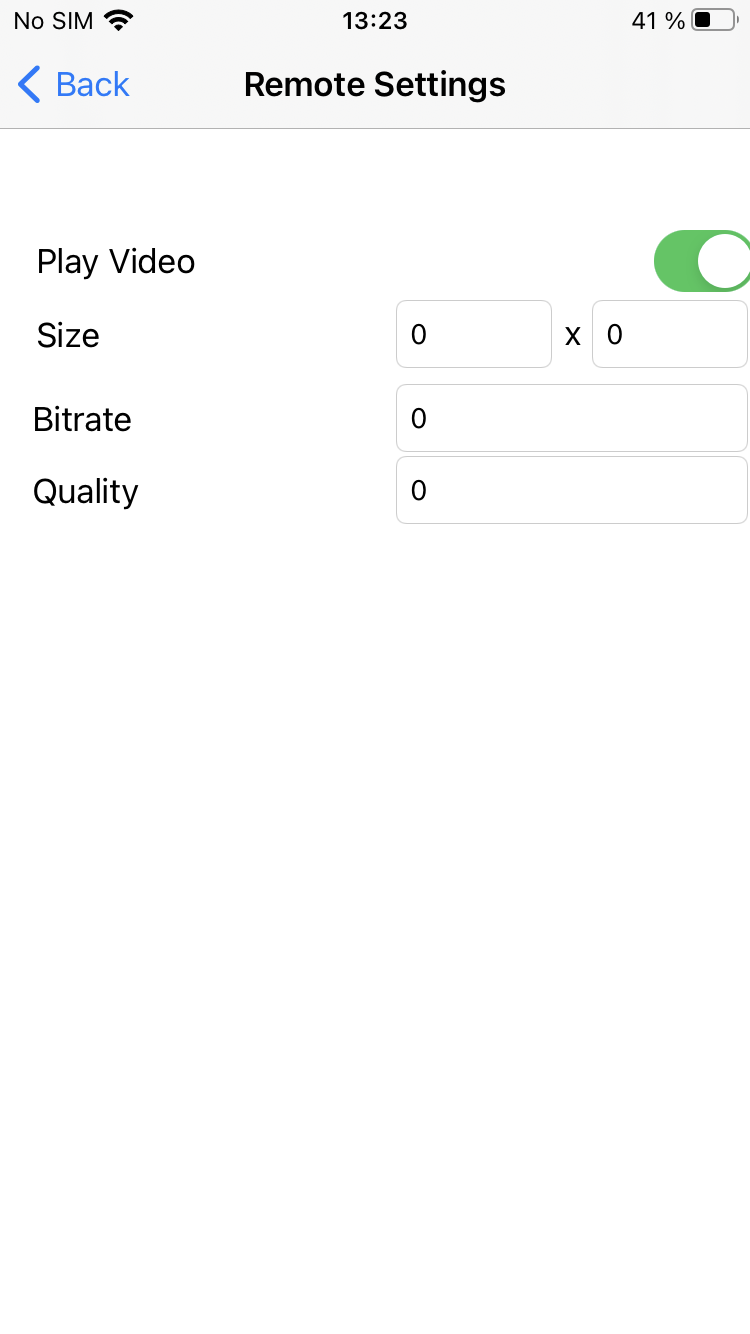
and view with controls for playback settings - when 'Remote settings' button is tapped.
Work with code of the example
To analyze the code, let's take MediaDevices example, which can be downloaded from GitHub.
View classes
- class for the main view of the application: ViewController (implementation file ViewController.swift)
- class for view with publishing settings: LocalViewController (implementation file LocalViewController.swift)
- class for view with playback settings: RemoteViewController (implementation file RemoteViewController.swift)
1. Import of API. code
import FPWCSApi2Swift
2. List available media devices.
WCSApi2.getMediaDevices code
localDevices = WCSApi2.getMediaDevices()
3. Default microphone and camera selection
FPWCSApi2MediaDeviceList.audio FPWCSApi2MediaDeviceList.video code
if (localDevices?.audio?.count ?? 0 > 0) {
microphone.text = (localDevices?.audio[0] as AnyObject).label
}
if (localDevices?.video?.count ?? 0 > 0) {
camera.text = (localDevices?.video[0] as AnyObject).label
}
4. Constraints for published stream.
FPWCSApi2AudioConstraints, FPWCSApi2AudioConstraints code
func toMediaConstraints() -> FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints {
let ret = FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints()
if (self.audioSend.isOn) {
let audio = FPWCSApi2AudioConstraints()
audio.useFEC = audioFEC.isOn
audio.useStereo = audioStereo.isOn
audio.bitrate = Int(audioBitrate.text ?? "0") ?? 0
ret.audio = audio
}
if (self.videoSend.isOn) {
let video = FPWCSApi2VideoConstraints()
for device in localDevices!.video {
if ((device as AnyObject).label == camera.text) {
video.deviceID = (device as AnyObject).deviceID;
}
}
video.minWidth = Int(videoWidth.text ?? "0") ?? 0
video.maxWidth = video.minWidth
video.minHeight = Int(videoHeight.text ?? "0") ?? 0
video.maxHeight = video.minHeight
video.minFrameRate = Int(videoFPS.text ?? "0") ?? 0
video.maxFrameRate = video.minFrameRate
video.bitrate = Int(videoBitrate.text ?? "0") ?? 0
ret.video = video;
}
return ret;
}
5. Constraints for played stream.
FPWCSApi2AudioConstraints, FPWCSApi2AudioConstraints code
func toMediaConstraints() -> FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints {
let ret = FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints();
ret.audio = FPWCSApi2AudioConstraints();
if (playVideo.isOn) {
let video = FPWCSApi2VideoConstraints();
video.minWidth = Int(videoWidth.text ?? "0") ?? 0
video.maxWidth = video.minWidth
video.minHeight = Int(videoHeight.text ?? "0") ?? 0
video.maxHeight = video.minWidth
video.bitrate = Int(videoBitrate.text ?? "0") ?? 0
video.quality = Int(videoQuality.text ?? "0") ?? 0
ret.video = video;
}
return ret;
}
6. Local camera and microphone testing
WCSApi2.getMediaAccess code
@IBAction func testPressed(_ sender: Any) {
if (testButton.title(for: .normal) == "TEST") {
let constraints = FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints(audio: true, video: true)!
do {
try WCSApi2.getMediaAccess(constraints, localDisplay.videoView)
} catch {
print(error)
}
testButton.setTitle("RELEASE", for: .normal)
} else {
WCSApi2.releaseLocalMedia(display: localDisplay.videoView);
testButton.setTitle("TEST", for: .normal)
}
}
7. Session creation and connection to the server.
WCSSession, WCSSession.connect code
The options include:
- URL of WCS server
- appKey of internal server-side application (defaultApp)
@IBAction func connectPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(connectButton, false)
if (connectButton.title(for: .normal) == "CONNECT") {
if (session == nil) {
let options = FPWCSApi2SessionOptions()
options.urlServer = urlField.text
options.appKey = "defaultApp"
do {
session = try WCSSession(options)
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
...
changeViewState(urlField, false)
session?.connect()
}
}
8. Stream publishing.
WCSSession.createStream, WCSStream.publish code
Object with the following stream options is passed to createStream method:
- stream name
- view to display video
- video constraints
@IBAction func publishPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(publishButton,false)
if (publishButton.title(for: .normal) == "PUBLISH") {
let options = FPWCSApi2StreamOptions()
options.name = publishName.text
options.display = localDisplay.videoView
options.constraints = localMediaConstrains;
do {
try publishStream = session!.createStream(options)
} catch {
print(error);
}
...
do {
try publishStream?.publish()
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
9. Preview stream playback
WCSSession.createStream, WCSStream.play code
Object with the following stream options is passed to createStream method:
- stream name
- view to display video
- video constraints
@IBAction func playPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(playButton,false)
if (playButton.title(for: .normal) == "PLAY") {
let options = FPWCSApi2StreamOptions()
options.name = playName.text;
options.display = remoteDisplay.videoView;
options.constraints = remoteMediaConstrains;
do {
playStream = try session!.createStream(options)
} catch {
print(error);
}
...
do {
try playStream?.play()
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
10. Stream playback stop.
WCSStream.stop code
@IBAction func playPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(playButton,false)
if (playButton.title(for: .normal) == "PLAY") {
...
} else{
do {
try playStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
11. Stream publishing stop.
WCSStream.stop code
@IBAction func publishPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(publishButton,false)
if (publishButton.title(for: .normal) == "PUBLISH") {
...
} else {
do {
try publishStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}