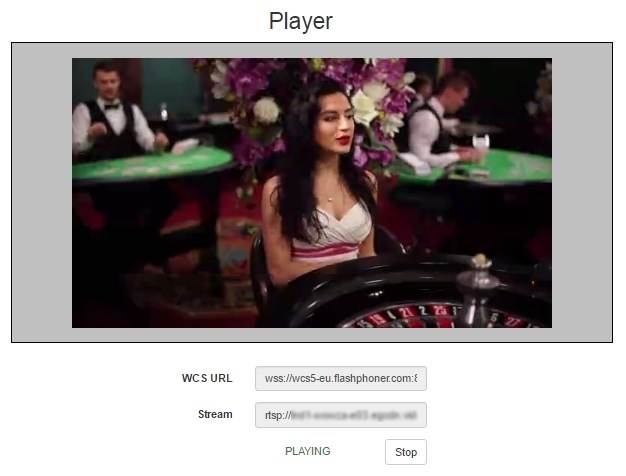
Player example
This player can be used to play any type of stream on Web Call Server
- RTSP
- WebRTC
- RTMP
- RTMFP
- SIP
On the screenshot below an RTSP stream is being playing in the web player.
Code of the example
The path to the source code of the example on WCS server is:
/usr/local/FlashphonerWebCallServer/client2/examples/demo/streaming/player
player.css - file with styles
player.html - page of the player
player.js - script providing functionality for the player
This example can be tested using the following address:
https://host:8888/client2/examples/demo/streaming/player/player.html
Here host is the address of the WCS server.
Work with code of the player
To analyze the code, let's take the version of file player.js with hash cf0daabc6b86e21d5a2f9e4605366c8b7f0d27eb, which is available here and can be
downloaded with corresponding build 0.3.18.1894.
1. Initialization of the API. line 8
API is initialized after loading the page. For Flash support, the path to SWF file is passed to the init() method.
Flashphoner.init({flashMediaProviderSwfLocation: '../../../../media-provider.swf'});
2. Connection to server. line 58
Connection to server is established when Start button is clicked.
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){
setStatus(session.status());
//session connected, start playback
playStream(session);
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){
setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED);
onStopped();
}).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){
setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED);
onStopped();
});
Session is created with method createSession(). Callback function, which will be called in case of successfully established connection
(status SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED), is added.
3. Playback of video stream. line 74
After establishing connection to the server, new video stream is created with method session.createStream(), and function play() is called to play
the stream.
When stream is created, the following parameters are passed
- streamName - name of the stream (rtsp:// address in this case)
- remoteVideo - <div> element, in which the video will be displayed
session.createStream({
name: streamName,
display: remoteVideo
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) {
document.getElementById(stream.id()).addEventListener('resize', function(event){
resizeVideo(event.target);
});
setStatus(stream.status());
onStarted(stream);
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() {
setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED);
onStopped();
}).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function() {
setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED);
onStopped();
}).play();
When stream is created, callback functions for events STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, STREAM_STATUS.FAILED can be added.
STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING - when this status is received, function resizeVideo() is called, which is used in the examples to adapt resolution to the element, in which the video will be displayed.
STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED and STREAM_STATUS.FAILED - when one of these statuses is received, function onStopped() of the example is called to make appropriate changes in controls of the interface.
4. Stop of playback. line 24
The following method is called to stop playback of video stream
stream.stop();
After calling the method, status STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED should arrive to confirm stop of playback from the server side.