iOS GPUImageDemo Swift¶
Пример приложения с захватом видео с использованием библиотеки GPUImage¶
Данное приложение демонстрирует возможность захвата видео из кастомного источника c использованием библиотеки GPUImage на Swift для применения фильтров.
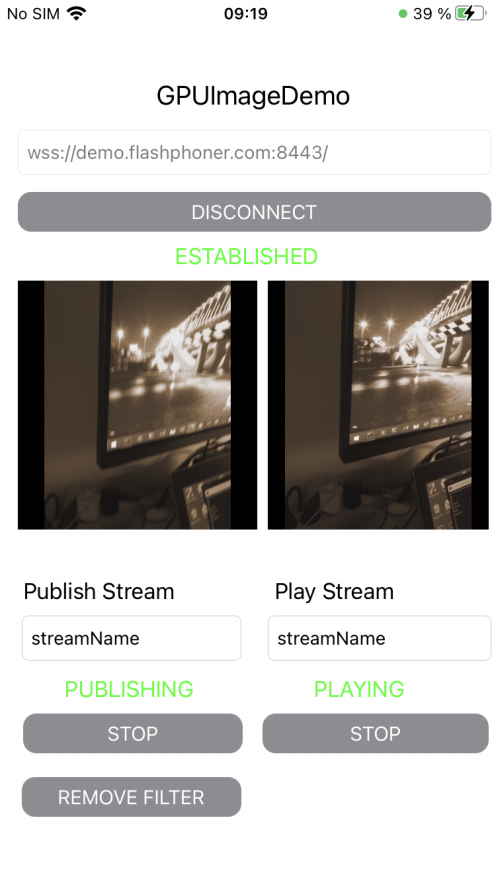
На скриншоте представлен пример публикации потока с фильтром MonochromeFilter из комплекта GPUImage
Поля ввода
WCS URL, гдеdemo.flashphoner.com- адрес WCS-сервераPublish Stream- для имени публикуемого потокаPlay Stream- для имени воспроизводимого потока
Кнопка Apply Filter/Remove Filter включает и отключает фильтр (на скриншоте фильтр включен)
Работа с кодом примера¶
Для разбора кода возьмем версию примера ImageOverlaySwift, которая доступна для скачивания на GitHub:
GPUImageDemoViewController- класс основного вида приложения (файл имплементации GPUImageDemoViewController.swift)CameraVideoCapturer- класс, реализующий захват и обработку видео (файл имплементации CameraVideoCapturer.swift)
1. Импорт API¶
2. Инициализация класса для захвата и обработки видео¶
3. Создание сессии и подключение к серверу.¶
WCSSession, WCSSession.connect code
В параметрах сессии указываются:
- URL WCS-сервера
- имя серверного REST hook приложения
defaultApp
@IBAction func connectPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(connectButton, false)
if (connectButton.title(for: .normal) == "CONNECT") {
if (session == nil) {
let options = FPWCSApi2SessionOptions()
options.urlServer = urlField.text
options.appKey = "defaultApp"
do {
try session = WCSSession(options)
} catch {
print(error)
}
}
...
changeViewState(urlField, false)
session?.connect()
} else {
session?.disconnect()
}
}
4. Публикация видеопотока¶
WCSSession.createStream, WCSStream.publish code
Методу createStream передаются параметры:
- имя публикуемого потока
- вид для локального отображения
- объект для захвата видео
@IBAction func publishPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(publishButton,false)
if (publishButton.title(for: .normal) == "PUBLISH") {
let options = FPWCSApi2StreamOptions()
options.name = publishName.text
options.display = localDisplay.videoView
options.constraints = FPWCSApi2MediaConstraints(audio: true, videoCapturer: capturer);
do {
publishStream = try session!.createStream(options)
} catch {
print(error);
}
...
do {
try publishStream?.publish()
capturer.startCapture()
} catch {
print(error);
}
} else {
do {
try publishStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
5. Воспроизведение видеопотока¶
WCSSession.createStream, WCSStream.play code
Методу createStream передаются параметры:
- имя воспроизводимого потока
- вид для отображения потока
@IBAction func playPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(playButton,false)
if (playButton.title(for: .normal) == "PLAY") {
let options = FPWCSApi2StreamOptions()
options.name = playName.text;
options.display = remoteDisplay.videoView;
do {
playStream = try session!.createStream(options)
} catch {
print(error)
}
...
do {
try playStream?.play()
} catch {
print(error);
}
} else{
do {
try playStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
6. Остановка воспроизведения видеопотока¶
WCSStream.stop code
@IBAction func playPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(playButton,false)
if (playButton.title(for: .normal) == "PLAY") {
...
} else{
do {
try playStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
7. Остановка публикации видеопотока¶
WCSStream.stop code
@IBAction func publishPressed(_ sender: Any) {
changeViewState(publishButton,false)
if (publishButton.title(for: .normal) == "PUBLISH") {
...
} else {
do {
try publishStream?.stop();
} catch {
print(error);
}
}
}
8. Вызов функции, применяющей фильтр¶
@IBAction func applyFilterPressed(_ sender: Any) {
if capturer.filter != nil {
capturer.applyFilter(nil)
applyFilterButton.setTitle("APPLY FILTER", for: .normal)
} else {
let filter = MonochromeFilter()
capturer.applyFilter(filter)
applyFilterButton.setTitle("REMOVE FILTER", for: .normal)
}
}
9. Применение фильтра¶
func applyFilter(_ filter: BasicOperation?) {
self.filter = filter
if let cam = self.camera, capturing {
cam.removeAllTargets()
self.gpuImageConsumer.removeSourceAtIndex(0)
if let fil = self.filter {
cam --> fil --> self.gpuImageConsumer
} else {
cam --> self.gpuImageConsumer
}
}
}
10. Получение очередного кадра от камеры¶
public func newTextureAvailable(_ texture:Texture, fromSourceIndex:UInt) {
// Ignore still ../images and other non-video updates (do I still need this?)
guard let frameTime = texture.timingStyle.timestamp?.asCMTime else { return }
// If two consecutive times with the same value are added to the movie, it aborts recording, so I bail on that case
guard (frameTime != previousFrameTime) else {
return
}
var pixelBufferFromPool:CVPixelBuffer? = nil
let pixelBufferStatus = CVPixelBufferCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault, texture.texture.width, texture.texture.height, kCVPixelFormatType_32BGRA, nil, &pixelBufferFromPool);
guard let pixelBuffer = pixelBufferFromPool, (pixelBufferStatus == kCVReturnSuccess) else {
return
}
CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, [])
renderIntoPixelBuffer(pixelBuffer, texture:texture)
capturer.captureOutput(pixelBuffer, time: frameTime)
CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(pixelBuffer, [])
}
11. Преобразование кадра в пиксельный буфер¶
func renderIntoPixelBuffer(_ pixelBuffer:CVPixelBuffer, texture:Texture) {
guard let pixelBufferBytes = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(pixelBuffer) else {
print("Could not get buffer bytes")
return
}
let mtlTexture = texture.texture;
guard let commandBuffer = sharedMetalRenderingDevice.commandQueue.makeCommandBuffer() else { fatalError("Could not create command buffer on image rendering.")}
commandBuffer.commit()
commandBuffer.waitUntilCompleted()
let bytesPerRow = CVPixelBufferGetBytesPerRow(pixelBuffer)
let region = MTLRegionMake2D(0, 0, mtlTexture.width, mtlTexture.height)
mtlTexture.getBytes(pixelBufferBytes, bytesPerRow: bytesPerRow, from: region, mipmapLevel: 0)
}