Taking a PNG snapshot of the stream¶
Overview¶
WCS provides a way to take a snapshot of the published stream using REST-queries as well as using JavaScript API.
Supported protocols¶
- WebRTC
- RTMP
- RTSP
Supported snapshot formats¶
- PNG
Operation flowchart¶
1: Using the REST query¶
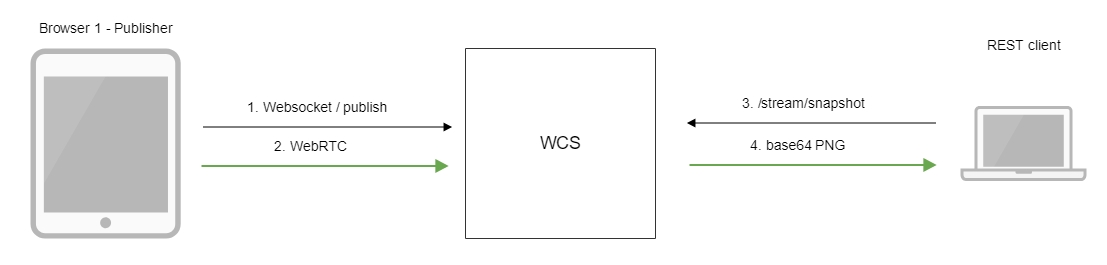
- The browser connects to the server via the Websocket protocol and sends the
publishStreamcommand. - The browser captures the microphone and the camera and sends the WebRTC stream to the server.
- The REST client sends to the WCS the
/stream/snapshotREST query. - The REST client receives a response with the base64-encoded snapshot of the stream.
2: Using JavaScript API¶
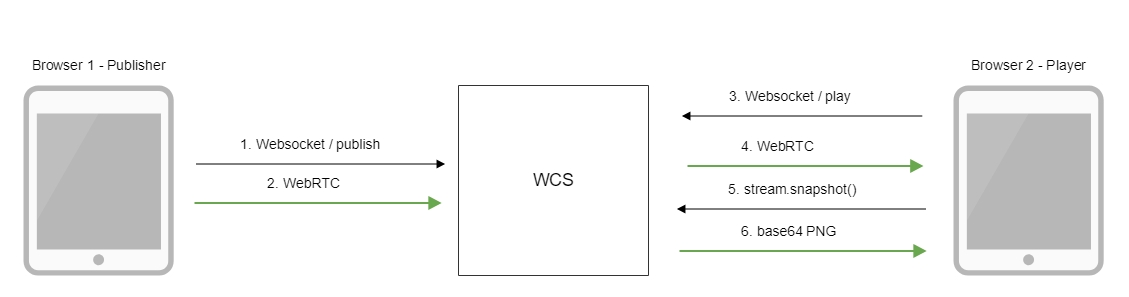
- The browser connects to the server via the Websocket protocol and sends the
publishStreamcommand. - The browser captures the microphone and the camera and sends the WebRTC stream to the server.
- The second browser establishes a connection also via Websocket and sends the
playStreamcommand. - The second browser receives the WebRTC stream and plays this stream on the page.
- The second browser invokes
stream.snapshot()to take a snapshot. - The second browser receives a response with the base64-encoded snapshot of the stream.
REST queries¶
WCS-server supports the /stream/snapshot REST method to take a snapshot.
A REST-query must be an HTTP/HTTPS POST request as follows:
- HTTP:
http://streaming.flashphoner.com:8081/rest-api/stream/snapshot - HTTPS:
https://streaming.flashphoner.com:8444/rest-api/stream/snapshot
Here:
streaming.flashphoner.com- is the address WCS server8081- is the standard REST / HTTP port of the WCS server8444- is the standard HTTPS portrest-api- is the required part of the URL/stream/snapshot- is the REST method used
REST-methods and response statuses¶
| REST-method | Request body | Response bosy | Response status |
|---|---|---|---|
| `/stream/snapshot` | 200 OK 404 Stream not found 500 Internal server error |
Parameters¶
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| streamName | Unique stream name | `64966f33` |
| data | Snapshot file encoded to base64 | `iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAUAAAADwCAYAAABxLb1rAAAACXBIWXMAAAAAAAAAAQCEeRdzAAAQA...` |
Sending the REST query to the WCS server¶
To send the REST query to the WCS server you need to use a REST-client.
Configuration¶
Since build 5.2.1116, a maximum snapshot taking duration, including a possible server disk I/O delay, may be configured when taking snapshot via REST API. By default, maximum duration is set to 3000 ms, and 30 checks if snapshot file is ready will be performed during this interval
If the snapshot file is not ready, and the interval is expired, /stream/snapshot request will return the following error
{
"exception": "com.flashphoner.rest.server.exception.InternalErrorException",
"reason": "com.flashphoner.rest.server.exception.InternalErrorException, Internal Server Error, Snapshot response timeout, ts: 1640836780816, path: /rest-api/stream/snapshot",
"path": "/rest-api/stream/snapshot",
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"message": "Snapshot response timeout",
"timestamp": 1640836780816,
"status": 500
}
JavaScript API¶
The snapshot method of the Stream object in WebSDK is intended to take stream snapshots. Example of use of this method can be found in the Stream Snapshot web applications that publishes a stream and take a snapshot.
-
Creating a new stream from the published stream
code:
-
Invoking the
snapshot()method
code:
-
Upon receiving the
SNAPSHOT_COMPLETEevent, thestream.getInfo()function returns the base64 encoded snapshot
code:
function snapshot(name) { setSnapshotStatus(); var session = Flashphoner.getSessions()[0]; session.createStream({name: name}).on(STREAM_STATUS.SNAPSHOT_COMPLETE, function(stream){ console.log("Snapshot complete"); setSnapshotStatus(STREAM_STATUS.SNAPSHOT_COMPLETE); snapshotImg.src = "data:image/png;base64,"+stream.getInfo(); ... } -
The stream stops
code:
function snapshot(name) { setSnapshotStatus(); var session = Flashphoner.getSessions()[0]; session.createStream({name: name}).on(STREAM_STATUS.SNAPSHOT_COMPLETE, function(stream){ ... stream.stop(); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream){ setSnapshotStatus(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED); console.log("Snapshot failed, info: " + stream.getInfo()); }).snapshot(); }
Quick manual on testing¶
- For the test we use:
- the demo server
demo.flashphoner.com; - the Chrome browser and the REST-client to send queries to the server;
- the Two Way Streaming web application to publish the stream;
-
the https://www.motobit.com/util/base64-decoder-encoder.asp service to decode the snapshot.
-
Open the page of the Two Way Streaming application. Click
Connect, then clickPublishto publish the stream:
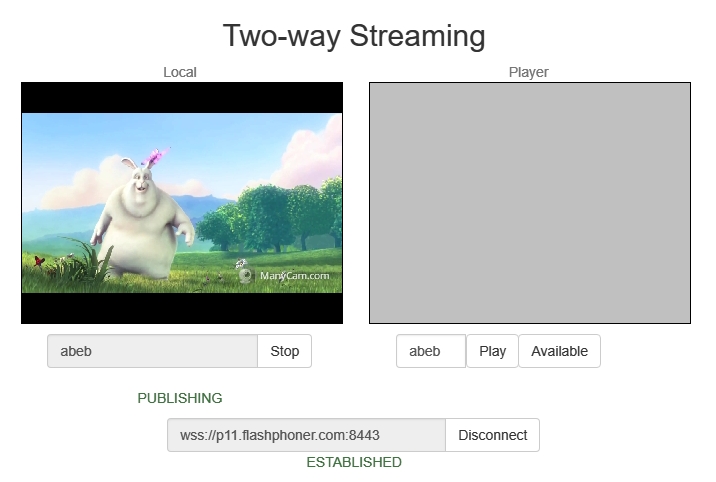
-
Open the REST-client. Send the /stream/snapshot query and pass the name of the published stream in parameters:
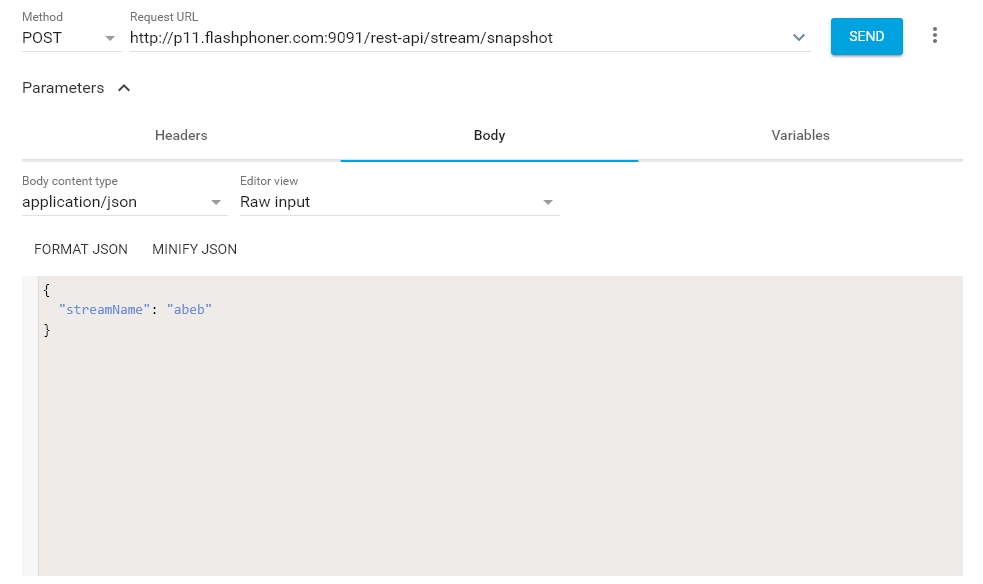
-
Make sure the response is received:

-
Open the online decoder and copy the response content to the form, then click
Convert the source data:
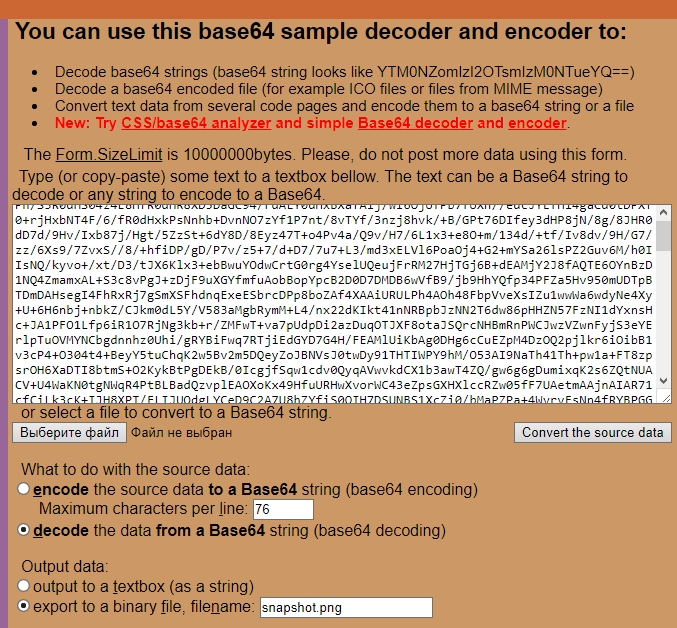
-
Here is the snapshot we have received:

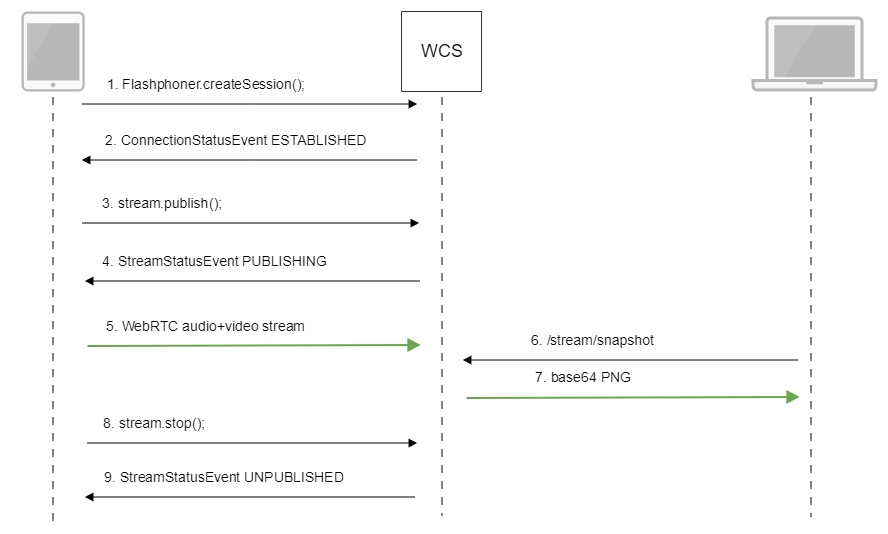
Call flow¶
Below is the call flow when using the Stream Snapshot example to publish the stream and take a snapshot
-
Establishing a connection to the server
Flashphoner.createSession()code
-
Receiving from the server and event confirming successful connection
SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHEDcode
-
Publishing the stream
stream.publish()code
-
Receiving from the server an event confirming successful publishing of the stream
STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHINGcode
session.createStream({ name: streamName, display: localVideo, cacheLocalResources: true, receiveVideo: false, receiveAudio: false }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function(publishStream){ setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING); onPublishing(publishStream); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function(){ ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream){ ... }).publish(); -
Sending the audio and video stream via WebRTC
-
Taking a snapshot of the broadcast. A new stream is created from the published one specially to take a snapshot
stream.snapshot()code
function snapshot(name) { setSnapshotStatus(); var session = Flashphoner.getSessions()[0]; session.createStream({name: name}).on(STREAM_STATUS.SNAPSHOT_COMPLETE, function(stream){ console.log("Snapshot complete"); setSnapshotStatus(STREAM_STATUS.SNAPSHOT_COMPLETE); snapshotImg.src = "data:image/png;base64,"+stream.getInfo(); //remove failed callback stream.on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(){}); //release stream object stream.stop(); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream){ setSnapshotStatus(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED); console.log("Snapshot failed, info: " + stream.getInfo()); }).snapshot(); } -
Stopping publishing the stream
stream.stop()code
-
Receiving from the server an event confirming unpublishing the stream
STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHEDcode
session.createStream({ name: streamName, display: localVideo, cacheLocalResources: true, receiveVideo: false, receiveAudio: false }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function(publishStream){ ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function(){ setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED); //enable start button onUnpublished(); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream){ ... }).publish();
Automatic stream snapshot taking¶
If necessary, snapshots for every stream published of supported format can be taken automatically. This feature can be enabled with the following parameter in flashphoner.properties file
Snapshot pictures placement can be set with the following parameter
In this folder, subfolder will be created for every stream. The subfolders name is formed from stream mediasession identifier (by default)
or stream name
Snapshot pictures are consistently numbered and are created periodically with the following setting
In this case, snapshot will be created from every 30 frame.
To save disk space, snspshot pictures amount can be limited using the following parameter
In this case, last 20 snapshot pictures will be stored in stream subfolder.
Snapshot pictures numeration will be continued if stream with same name vis published.