To another WCS server via WebRTC¶
Overview¶
WCS can rebroadcast a video stream via WebRTC to another WCS server on demand. Republishing of a WebRTC stream is managed by the REST API.
Operation flowchart¶
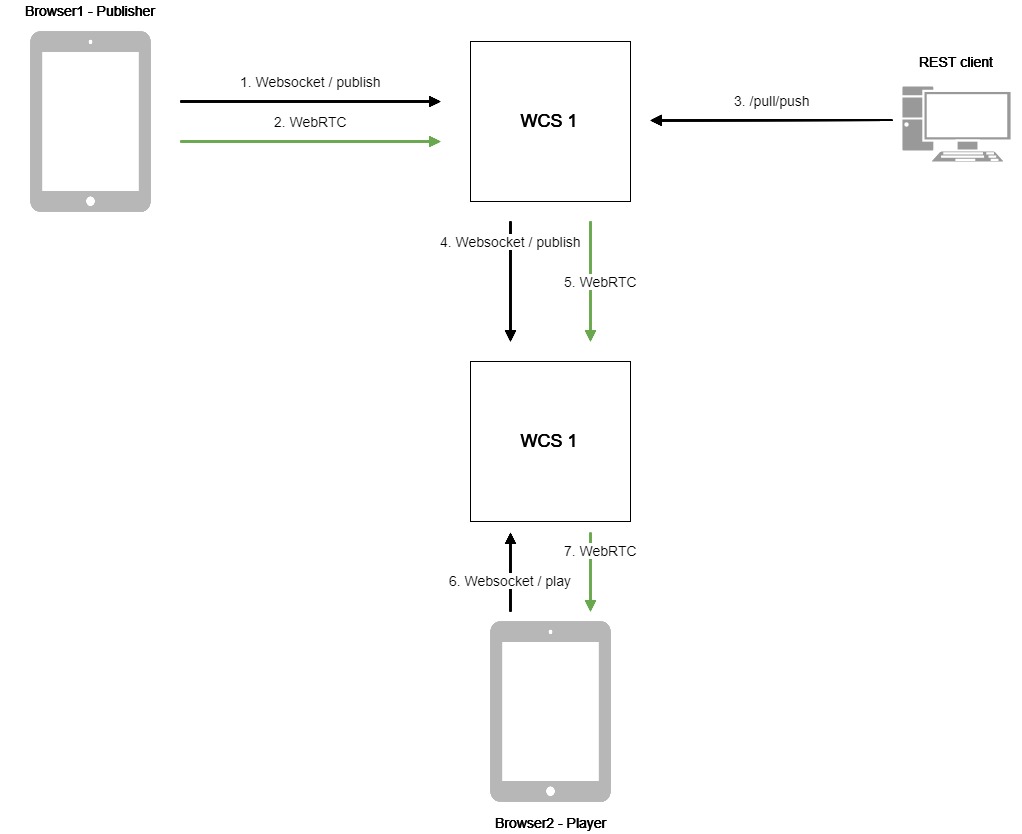
- The browser connects to the WCS1 server via the Websocket protocol and sends the
publishStreamcommand. - The browser captures the microphone and the camera and send the WebRTC stream to the server.
- The REST client sends to the WCS1 server the
/pull/pushquery. - WCS1 publishes the stream to WCS2.
- WCS2 receives the WebRTC stream from WCS1.
- The second browser establishes a connection to the WCS2 server via Websocket and sends the
playStreamcommand. - The second browser receives the WebRTC stream and plays this stream on the page.
REST API¶
A REST query must be an HTTP/HTTPS POST query in the following form:
- HTTP:
http://test.flashphoner.com:8081/rest-api/pull/push - HTTPS:
https://test.flashphoner.com:8444/rest-api/pull/push
Where:
streaming.flashphoner.com- is the address of the WCS server8081- is the standard REST / HTTP port of the WCS server8444- is the standard HTTPS portrest-api- is the required prefix/pull/push- is the REST-method used
REST methods and responses¶
| REST method | Request body | Response body | Response status | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| `/pull/push` | 409 Conflict 500 Internal error | Broadcasts the WebRTC stream to the specified URL | ||
| `/pull/find_all` | 404 Not found 500 Internal error | Find all pulled streams | ||
| `/pull/terminate` | 404 Not found 500 Internal error | Terminate a pulled stream |
Parameters¶
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| uri | URL of the WebRTC stream | `wss://demo.flashphoner.com:8443/websocket` |
| localMediaSessionId | Session identifier | `5a072377-73c1-4caf-abd3` |
| remoteMediaSessionId | Identifier of the session on the remote server | `12345678-abcd-dead-beaf` |
| localStreamName | Local name assigned to the captured stream. The stream can be fetched from the WCS server using this name | `testStream` |
| remoteStreamName | Name of the captured stream on the remore server | `testStream` |
| status | Current status of the stream | `NEW` |
Configuration¶
By default, WebRTC stream is pulled over unsecure Websocket connection, i.e. WCS server URL has to be set as ws://demo.flashphoner.com:8080. To use Secure Websocket, the parameter must be set in file flashphoner.properties
This change has to be made on both WCS servers: the server that publishes the stream and the server the stream is pushed to.
Quick manual on testing¶
- For this test we use:
- two WCS servers;
- the Chrome browser and the REST client to send queries to the server;
- the Two Way Streaming web application to publish the stream;
-
the Player web application to play the captured stream in a browser.
-
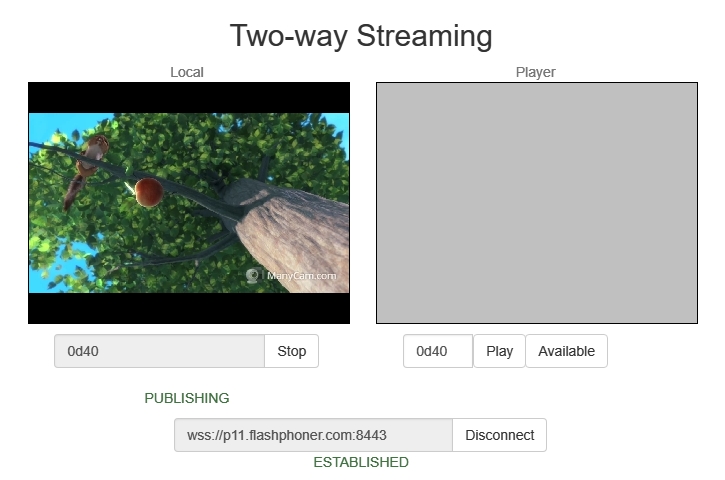
Open the Two Way Streaming web application, publish the stream on the server
-
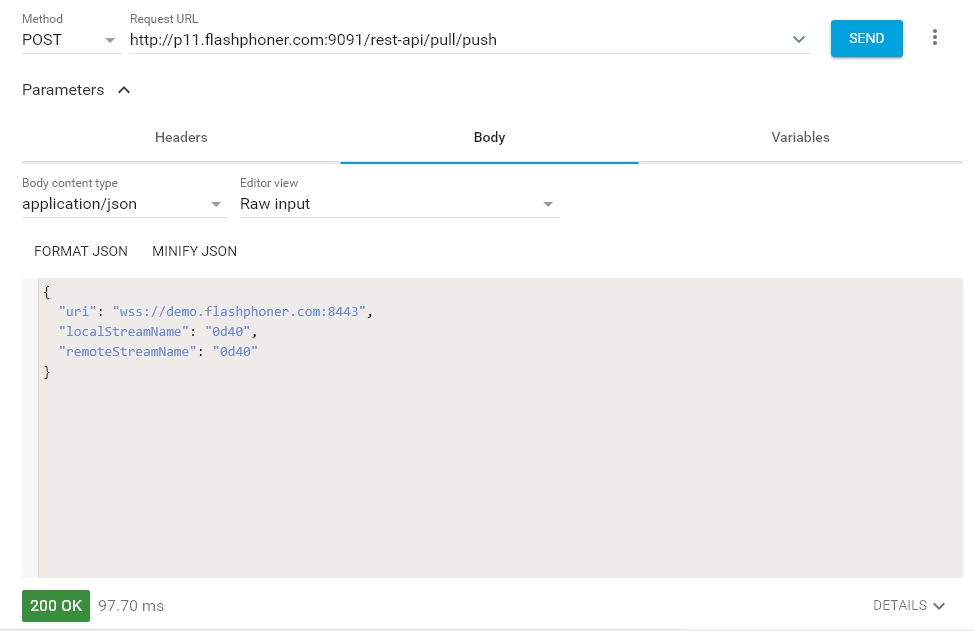
Open the REST client. Send the
/pull/pushquery and specify in its parameters: - the URL of the WCS server the stream is captured from
- the name of the stream published on the server
-
the local name of the stream
-
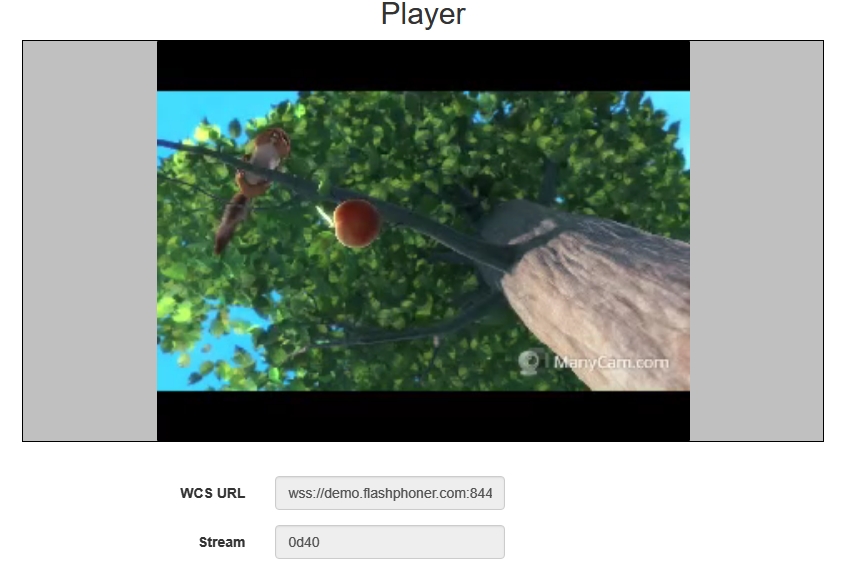
Open the Player web application and specify the local stream name in the
Streamfield, then clickStart
Call flow¶
Below is the call flow when using the Two Way Streaming example to publish a stream on one WCS server and the Player example to play that stream on another WCS server.
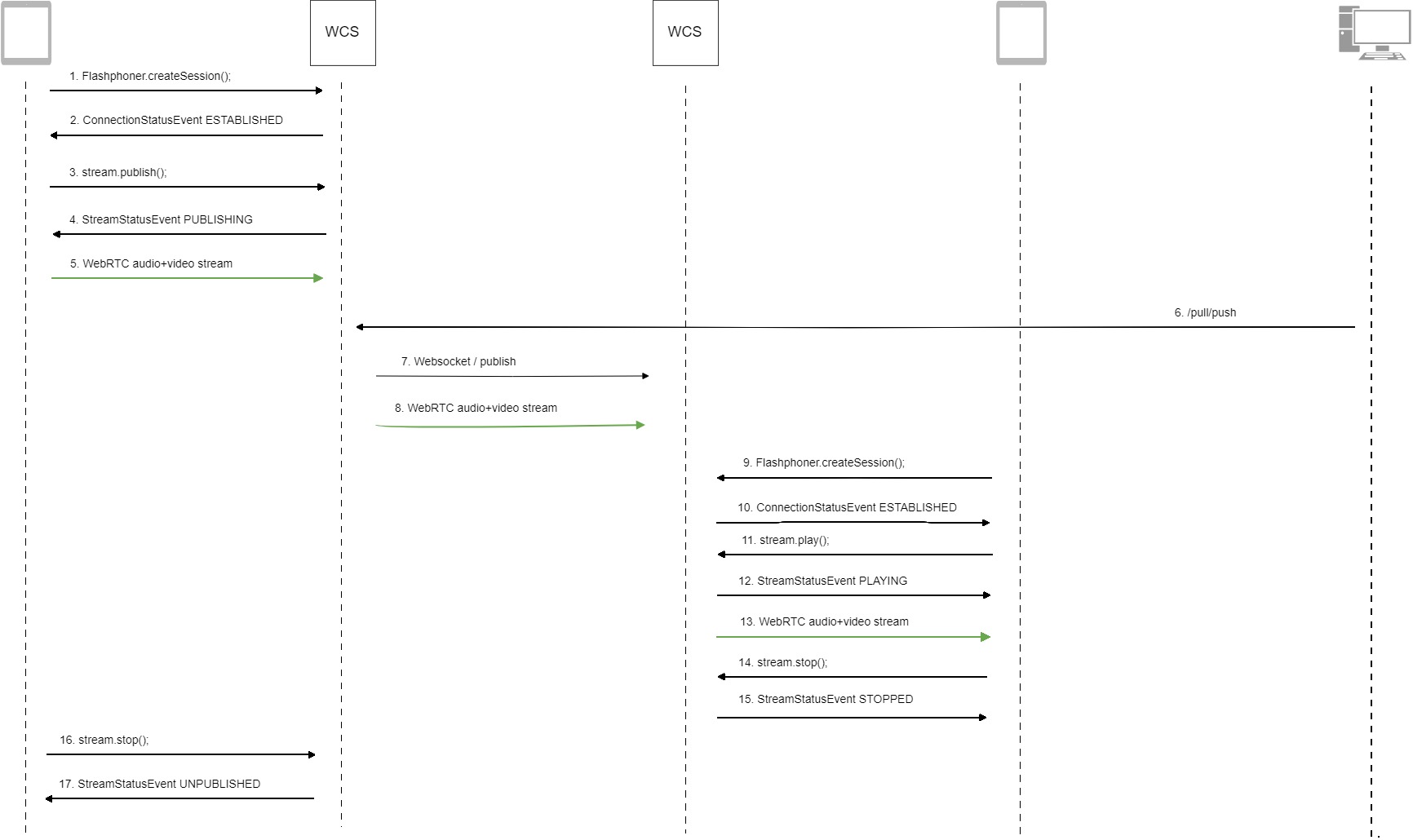
-
Establishing a connection to the server
Flashphoner.createSession()code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function (session) { setStatus("#connectStatus", session.status()); onConnected(session); }).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function () { setStatus("#connectStatus", SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED); onDisconnected(); }).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function () { setStatus("#connectStatus", SESSION_STATUS.FAILED); onDisconnected(); }); -
Receiving from the server an event confirming successful connection
SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHEDcode
-
Publishing the stream
Stream.publish()code
-
Receiving from the server an event confirming successful publishing of the stream
STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHINGcode
session.createStream({ name: streamName, display: localVideo, cacheLocalResources: true, receiveVideo: false, receiveAudio: false }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) { setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING); onPublishing(stream); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function () { ... }).publish(); -
Sending the audio-video stream via WebRTC to the server
-
Sending the
/pull/pushREST query to the server -
Publishing the stream on the second server
-
Sending the audio-video stream via WebRTC to the second server
-
Establishing a connection to the second server
Flashphoner.createSession()code
Flashphoner.createSession({urlServer: url}).on(SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHED, function(session){ setStatus(session.status()); //session connected, start playback playStream(session); }).on(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED, function(){ setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.DISCONNECTED); onStopped(); }).on(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED, function(){ setStatus(SESSION_STATUS.FAILED); onStopped(); }); -
Receiving from the server an event confirming successful connection
SESSION_STATUS.ESTABLISHEDcode
-
Requesting to play the stream
Stream.play()code
-
Receiving from the server an event that confirms successful capturing and playing of the stream
STREAM_STATUS.PLAYINGcode
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) { $("#preloader").show(); setStatus(stream.status()); onStarted(stream); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.NOT_ENOUGH_BANDWIDTH, function(stream){ ... }); stream.play(); -
Sending the audio-video stream via WebRTC
-
Stopping the playback of the stream
Stream.stop()code
-
Receiving from the server an event confirming the playback of the stream is stopped
STRTEAM_STATUS.STOPPEDcode
stream = session.createStream(options).on(STREAM_STATUS.PENDING, function(stream) { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PLAYING, function(stream) { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED, function() { setStatus(STREAM_STATUS.STOPPED); onStopped(); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function(stream) { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.NOT_ENOUGH_BANDWIDTH, function(stream){ ... }); stream.play(); -
Stopping publishing the stream
Stream.stop()code
-
Receiving from the server an event that confirms unpublishing of the stream
STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHEDcode
session.createStream({ name: streamName, display: localVideo, cacheLocalResources: true, receiveVideo: false, receiveAudio: false }).on(STREAM_STATUS.PUBLISHING, function (stream) { ... }).on(STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED, function () { setStatus("#publishStatus", STREAM_STATUS.UNPUBLISHED); onUnpublished(); }).on(STREAM_STATUS.FAILED, function () { ... }).publish();